Introduction
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is the most common form of SCID. It is caused by mutations in the
IL2RG gene, and involves both the humoral and cell-mediated immune system, with typical absence of both T cells and natural killer (NK) cells. With respect to its clinical presentation, X-linked SCID typically presents in early infancy with failure to thrive, chronic diarrhea, opportunistic infections, and fatality in the first 2 years of life without immune reconstitution (
Buckley 2004;
van der Burg and Gennery 2011). The average incidence of SCID has been quoted at 1 in 66,250 (
Kwan et al. 2013). In 2013, Ontario began screening for SCID as part of the routine newborn screening with the goal of improving early diagnosis and intervention (
Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care 2013).
The
IL2RG gene encodes the γ
c portion of the IL-2 receptor, which along with IL-2Rα and IL-2Rβ makes up the entire IL-2 receptor. The γ
c portion interacts with the IL-2 cytokine, and it has fundamental function in the development of regulatory T cells, maintaining peripheral tolerance, as well as increasing the cytolytic activity of NK cells (reviewed in
Kovanen and Leonard (2004)). The γ
c portion is also involved in the signaling of various other cytokines including IL-4, IL-7 (
Kawahara et al. 1994), IL-9 (
Russell et al. 1994), IL-15 (
Giri et al. 1994), and IL-21 (
Ozaki et al. 2002). IL-7 has been shown to be important for lymphocyte homeostasis and B-cell development, whereas IL-15 is fundamental in the development of NK cells, as mice deficient in IL-15 lack both NK cells and CD8
+ T cells (
Kennedy et al. 2000;
Lodolce et al. 1998). Finally, IL-4 and IL-21 have been implicated in T-helper cell differentiation as well as the synthesis of immunoglobulins (reviewed in
Kovanen and Leonard (2004)). Taken together, these findings provide evidence that γ
c is fundamental for the development and function of T, B, and NK cells (
Kovanen and Leonard 2004).
Mutations in the
IL2RG gene leading to X-linked SCID were first described in 1993 (
Noguchi et al. 1993;
Puck et al. 1993) and since then, there have been 200 mutations in the 8 exons of the
IL2RG gene catalogued, of which the majority (119) are frameshift mutations (
Kattman and Puck 2012).
An understanding of the genetic mutation as well as the corresponding phenotype is fundamental. Mutational analysis has revealed that there are parts of the gene prone to mutation; these are known as hotspots (
Puck et al. 1993). In addition, genotype/phenotype correlations have been revealed as evidenced most strikingly by the R222C mutation of
IL2RG mutation (
Fuchs et al. 2014;
Sharfe et al. 1997). The R222C mutation of
IL2RG leading to a SCID phenotype presented atypically with a normal thymus gland, mitogen response, as well as normal numbers of T and B cells. However, despite having a normal number and repertoire of T cells, the T cells were found to have a reduced ability to bind to IL-2. Interestingly, the index case presented with
P. jiroveci pneumonia at 9 months of age, in keeping with an underlying immunodeficiency (
Sharfe et al. 1997). This finding provides evidence that different genetic mutations in the
IL2RG can lead to variable SCID phenotypes. In this study, we sought to further the knowledge of specific mutations in the
IL2RG, through a description of 3 novel mutations in the
IL2RG gene and the associated phenotype.
Discussion
We describe 3 novel mutations in the IL2RG gene leading to SCID phenotypes.
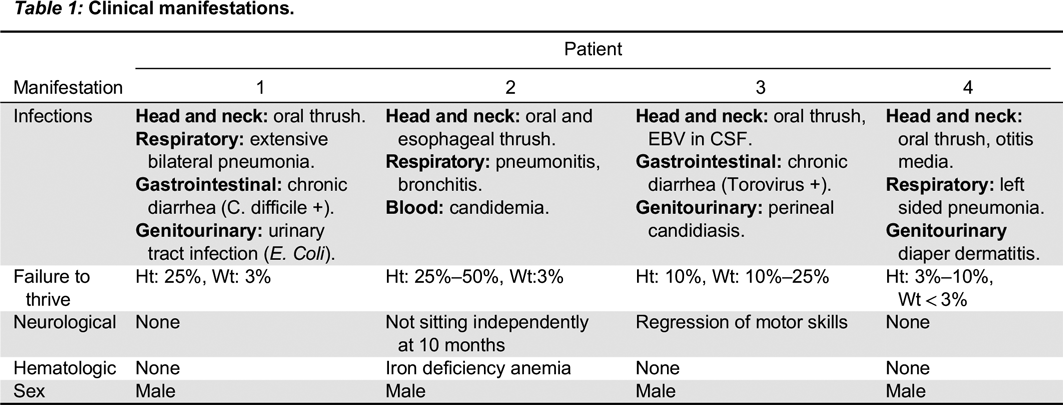
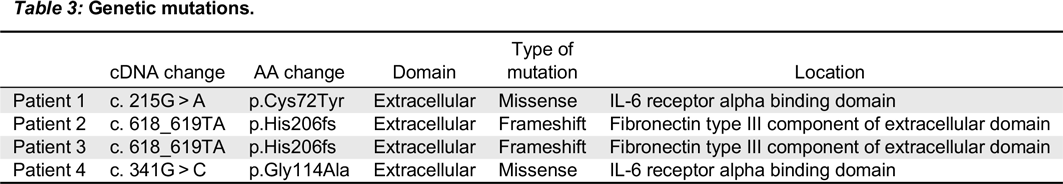
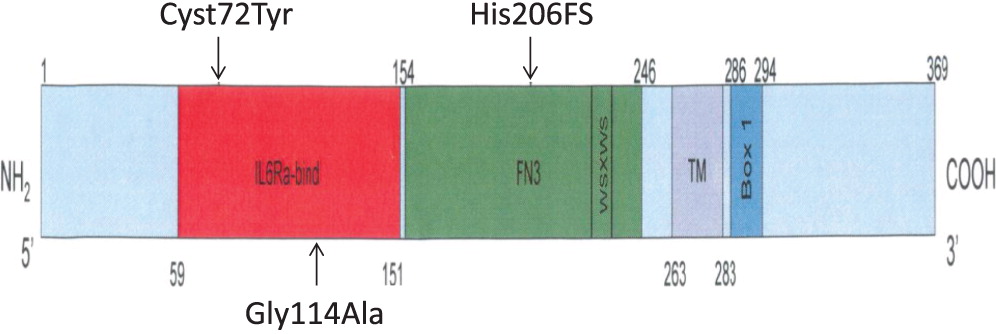
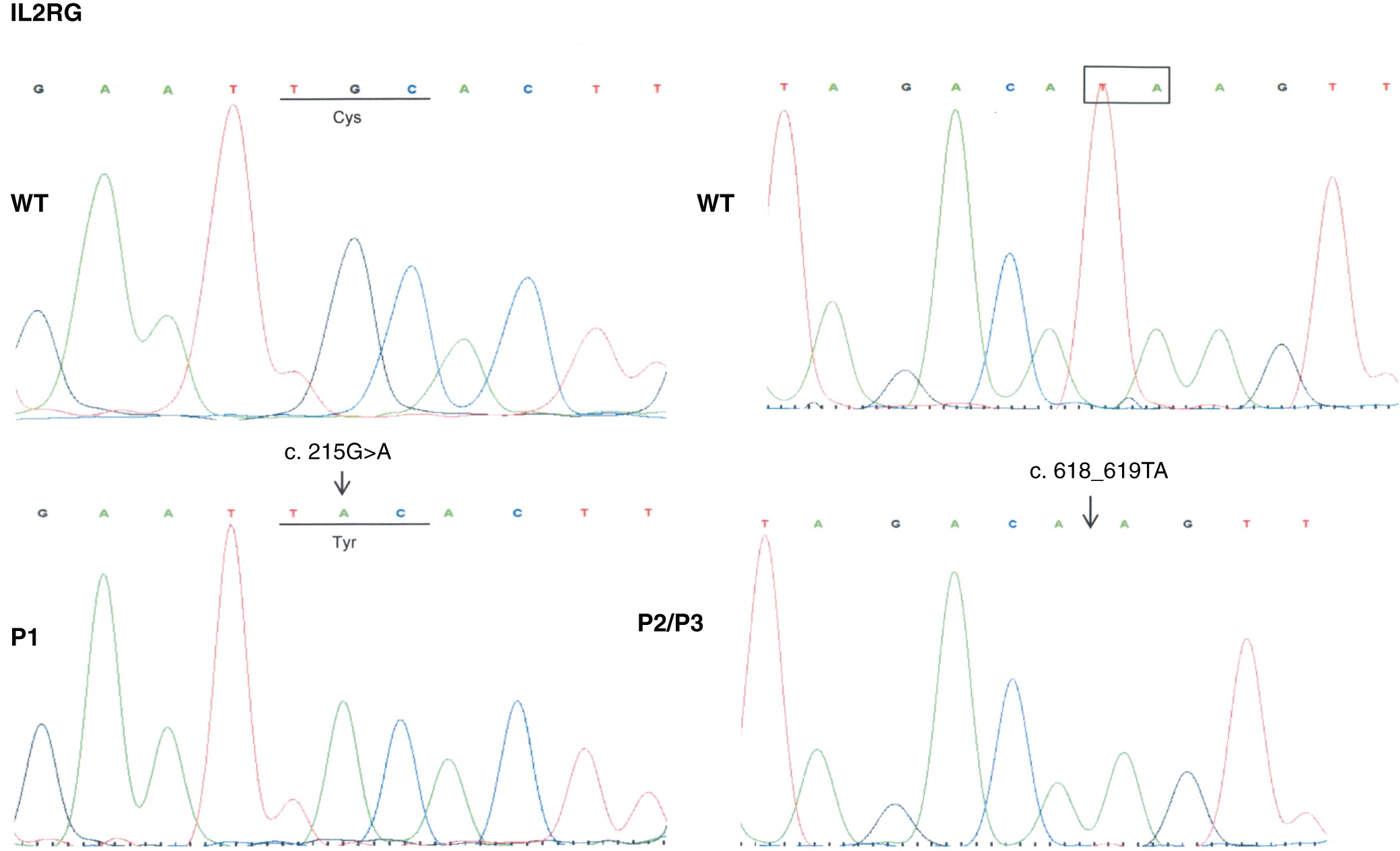
In the first mutation, Patient 1 had a c. 215 G > A substitution, which predicts a p.Cys72Tyr in the extracellular domain. This corresponded to a phenotype of T
− B
+ NK
−, in keeping with a typical X-linked SCID phenotype. Typically, mutations in
IL2RG lead to a T
− NK
− phenotype, as the development and growth of both T and NK cells depend on various cytokines including IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-15, and IL-21 all of which signal through the γ
c receptor (
Giri et al. 1994;
Kawahara et al. 1994;
Russell et al. 1994;
Ozaki et al. 2002). A lack of NK cells in mutations in the γ
c receptor are thought to be secondary to impaired IL-15 signaling, as mice deficient in the IL-15 receptor alpha subunit have a significant block in NK-cell development (
Lodolce et al. 1998;
Notarangelo et al. 2000).
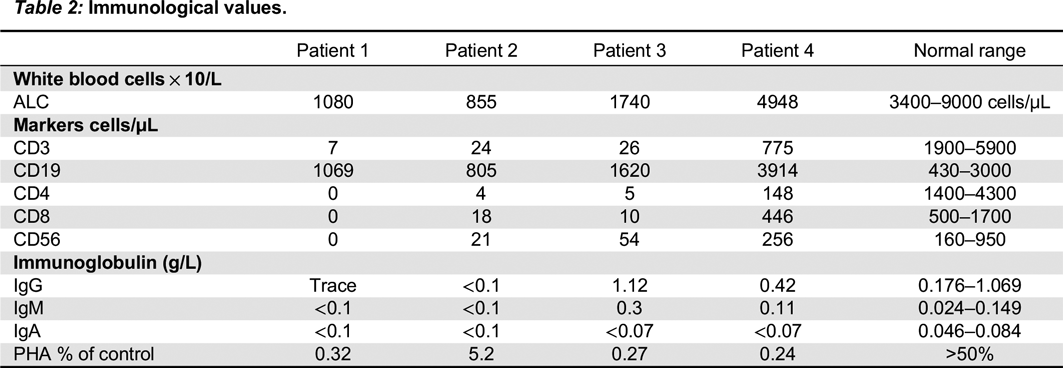
In the second mutation, a c. 618_619TA in exon 5 lead to a p.His206fs deletion. Both patients had similar clinical presentations. Specifically, both Patients 2 and 3 were noted to have classic SCID presentations of fungal infections with candidiasis, viral infections, chronic diarrhea, as well as failure to thrive. With respect to their laboratory findings, both patients had a low number of absolute lymphocytes, T cells, and their lymphocytes were comprised of mostly B cells. Taken together, these data provide evidence that a frameshift at position 206 leads also to a typical IL2RG SCID phenotype. This provides evidence of a strong genotype and phenotype correlation between Patients 2 and 3.
In the last mutation, Patient 4 had c. 341 G > C in exon 3, which predicts a p.Gly114Ala substitution in the extracellular domain. The phenotype was characterized as a T
+ B
− NK
+. We note that he did have evidence of some maternal engraftment. Interestingly, Puck et al. (
1993) described a different missense mutation at this site with a p.Gly114Ala mutation (cDNA position 355 exon 3). The patient did produce the
IL2RG mRNA which, supports that this mutational site could possibly lead to a presentation of leaky SCID. There are a variety of causes of T
+ SCID including Omenn’s syndrome (reviewed in (
Villa et al. 2008) and maternal engraftment. Some degree of maternal engraftment is common in SCID. In a series of 121 SCID patients, some maternally engrafted cells were detected in 48 patients (
Muller et al. 2001). Furthermore, a late presentation of X-linked SCID was described secondary to revertant somatic mosaicism (
Stephan et al. 1996), and more recently, this phenomenon has been described with a mutation in the P58T region of the
IL2RG (
Okuno et al. 2015). In our patient, it is not possible to say which proportions of his cells were of maternal origin versus possibly a leaky phenotype. Therefore we will explore some other examples of T
+ SCID.
T
+ SCID has been described in other cases of
IL2RG mutations. The R222C mutation, is a notable example of this phenomenon (
Sharfe et al. 1997). As previously mentioned, the patient presented with
pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia at 9 months of age and had normal T-cell, B-cell, and NK-cell numbers, a complete T-cell repertoire and normal response to mitogenic stimulation. However, the patient did not respond to exogenous IL-2, despite having normal expression levels of the IL2RG protein. The patient was found to have an altered IL-2 binding site leading to a reduced affinity for IL-2 binding, and subsequent downstream activation of the Janus kinase 3 pathway (
Sharfe et al. 1997). A follow-up report described more patients with this mutation, and stressed that
IL2RG R222C mutation needs to be ruled out in children with clinical features of SCID, even in the absence of typical laboratory data (
Somech and Roifman 2005). Further studies on the R222C mutation confirmed the findings of the functional impairment in T-cell response to IL-2. They also found that for NK cells, IL-2 mediated NK-cell degranulation, as well as IL-15 induced cytokine expression was significantly reduced (
Fuchs et al. 2014). Recently, a different mutation in the
IL2RG was described leading to a similar T
+ SCID phenotype. A 12-base pair intronic deletion, c609-15_609-4del12 was described in a T
+ B
− NK
− X-linked SCID patient (
Gray et al. 2015). The patient had mild T-cell lymphopenia, normal T-cell receptor diversity, a reduced PHA stimulation, and no evidence of chimerism. This deletion lead to a splicing defect and a subsequent truncated
IL2RG mRNA, with normal IL-2Rγ expression. There was also complete absence of IL-2 and IL-7 mediated STAT5 phosphorylation (
Gray et al. 2015). Taken together, these findings provide evidence that mutations in the
IL2RG can lead to a T
+ SCID with normal or mildly reduced numbers of T cells, but impairment in IL-2 mediated downstream signaling cascades that are vital to T-cell function.
The presence of normal numbers of NK cells in patient 4 deserves discussion. NK cells of maternal origin have been reported in
IL2RG deficiency. Recently,
Estevez et al. (2014) described a case of an 8-month-old boy who presented with diarrhea and dehydration and was found to have
S. auricularis,
S. epidermidis, and
C. parasilopsis in the blood cultures, with stool cultures positive for both
C. albicans and
P. aeruginosa. The patient was subsequently found to have an ACC insertion in exon 5, of
IL2RG, with a phenotype of T
− B
+ NK
+, and he was shown to have maternally derived NK cells. Normal numbers of NK cells have been seen in some previous
IL2RG mutations. Enumeration of NK cells was normal in all reports of R222C (
Fuchs et al. 2014). Additionally, there have been a few reports of the presence of NK cells in patients with mutations involving the γ
c portion of the
IL2RG and these have raised the possibility of a potential downstream activation mechanism in NK cell differentiation. In one case report, a patient with a mutation in exon 5 with a c.691G > A corresponding to a R226H substitution, had increased NK cells (59.5%) with an erythroderma-like skin reactive characterized by infiltration of CD56
+ cells. These were not maternal in origin as evidenced by the microsatellite polymorphism analysis where the allelic patterns from the patient were distinct from maternal ones (
Shibata et al. 2007). A second case report described a mutation in a splice site region in intron 3, leading to 2 alternatively spliced mRNAs and undetectable γ
c levels. The patient, however, had near normal numbers of NK cells with a genotype of T
− B
+ NK
+. From this study, the authors concluded that the IL-15 receptor-mediated signaling is preferentially retained when γ
c levels are depleted (
Ginn et al. 2004). Taken together, these reports suggest that NK cells in
IL2RG deficiency may be of maternal origin, but also that there may be downstream pathways for the activation and differentiation of NK cells in γ
c deficiency, and that not all detectable NK cells in the
IL2RG deficiency are of maternal origin. Further studies will need to further characterize the mutations and their implications on T and NK cells.
In conclusion, we described 3 novel mutations in the IL2RG gene leading to various phenotypic presentations of X-linked SCID. We identified a mutation with a p.Cys72Tyr substitution, which was in keeping with the typical phenotype findings of X-linked SCID. In the second mutation, a deletion of p.His206fs, both Patient B and C were found to have SCID presentations with very low T and NK cells. Finally, we described a novel missense mutation leading to a p.Gly114Ala substitution, which presented as a T+ NK+ SCID. This finding further strengthens the knowledge that patients with IL2RG mutations can have atypical presentations. These descriptions of 3 novel mutations contribute to the molecular understanding of IL2RG. Future studies will need to address the p.Gly114Ala mutation and its effect on IL-2 mediated downstream signaling cascades.