C-reactive protein and other biomarkers—the sense and non-sense of using inflammation biomarkers for the diagnosis of severe bacterial infection
Abstract
Biomarker
Definition and expectations
Interpretation of studies on biomarkers
Inflammation
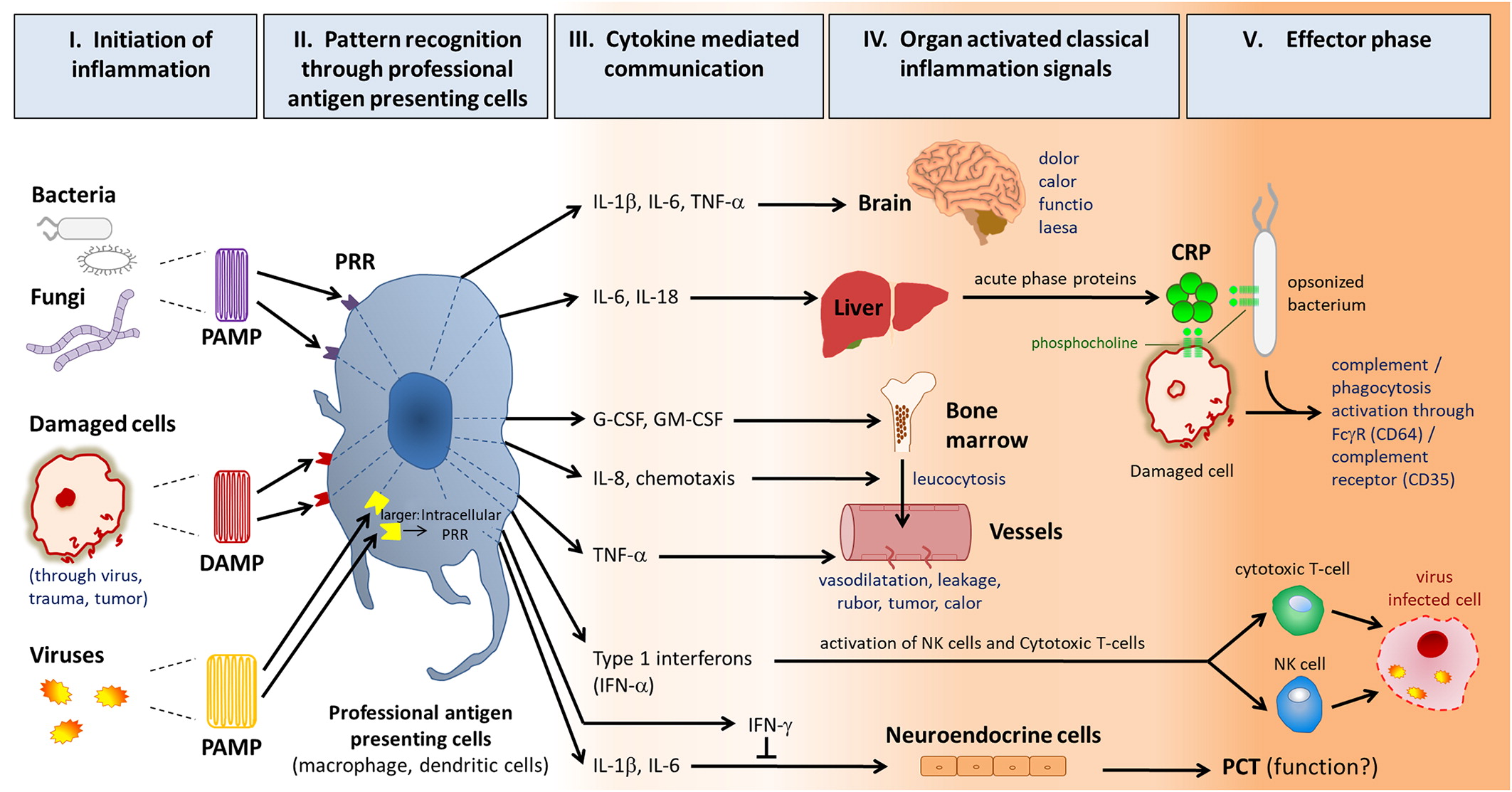
Significance of biomarkers regarding the differentiation between bacterial and non-bacterial infections

Note: Frequencies are not given with greater precision because there is great variability in reported frequencies of fever (depending on definition and method of measurement), pathogens (depending on patient group and setting—practice, emergency room, or hospital), and SBI (depending on prior treatment in peripartal period, vaccination status). The frequency may differ between countries.
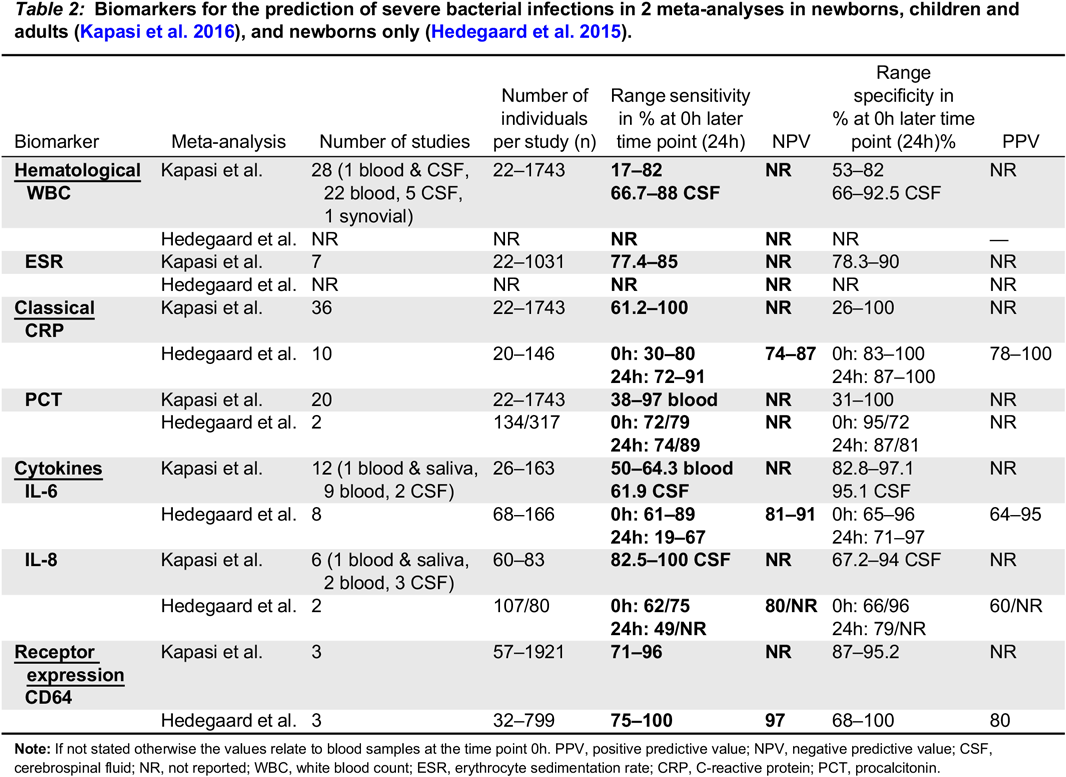
Note: If not stated otherwise the values relate to blood samples at the time point 0h. PPV, positive predictive value; NPV, negative predictive value; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; NR, not reported; WBC, white blood count; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP, C-reactive protein; PCT, procalcitonin.
Classical inflammatory markers
C-reactive protein and procalcitonin
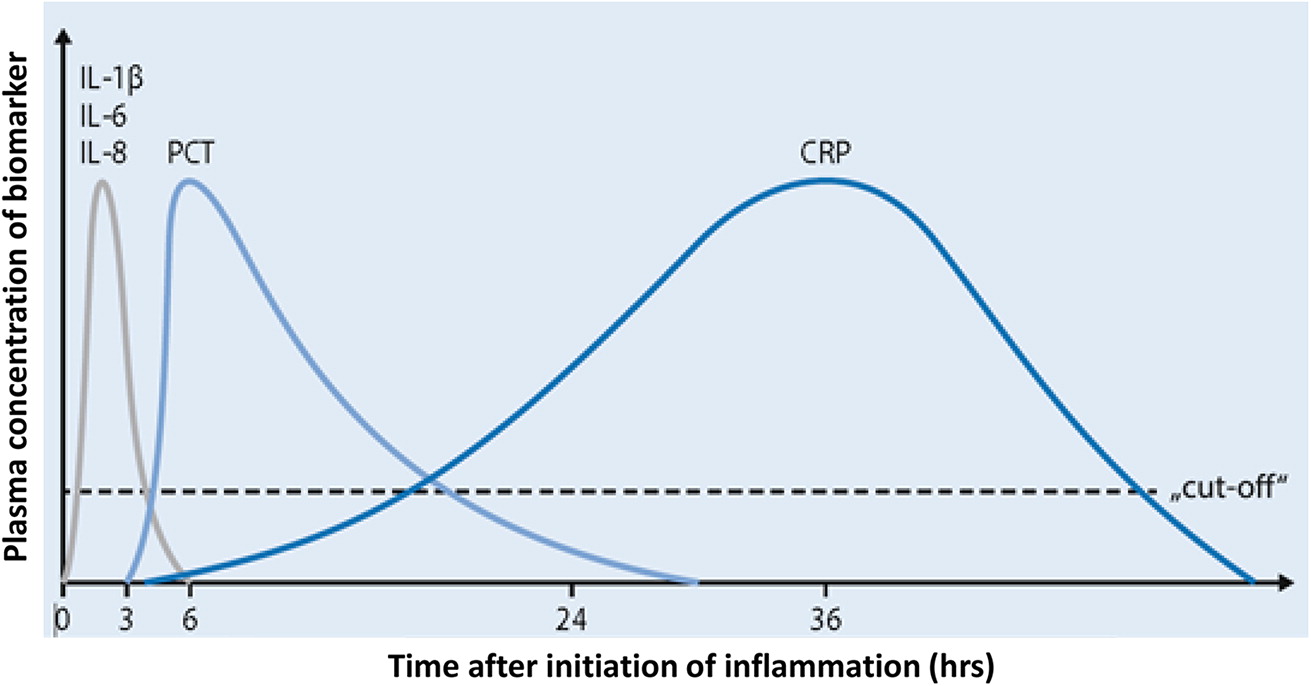

Note: Risk estimation predominantly following clinical biometric biomarkers in combination with laboratory biomarkers (adapted from Niehues 2013).
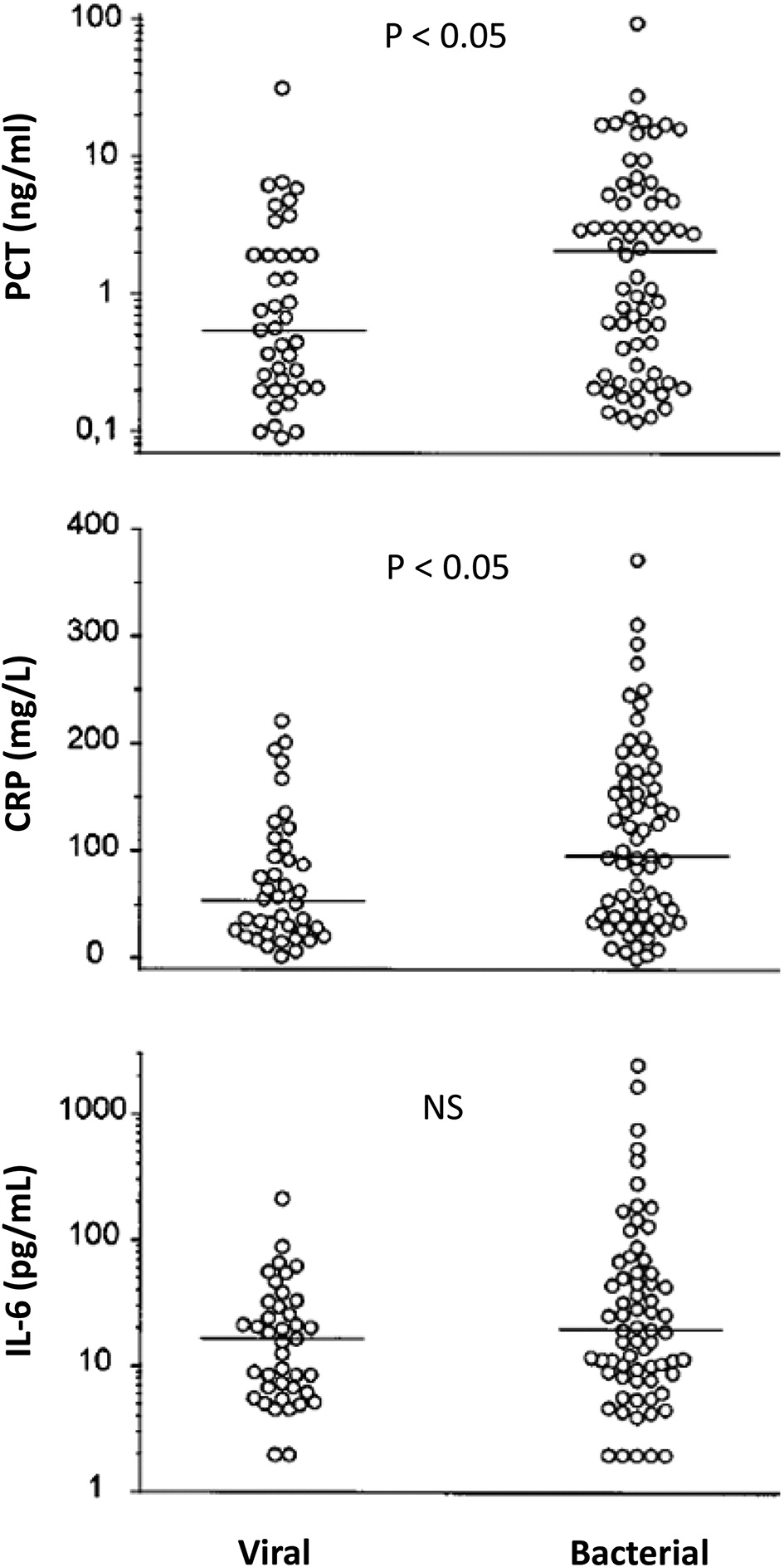
Is procalcitonin superior to CRP for SBI detection?
Cytokine biomarkers
Hematological biomarkers
Clinical biometric markers
Management of infections in different settings
Is a general screening with laboratory biomarkers useful in the GP office or in the Emergency room?
Significance for using laboratory biomarkers in monitoring disease courses and steering antibiotic therapy
Use of cytokines and classical inflammatory biomarkers in special conditions such as fever and cytopenia
Novel technologies
Summary and outlook
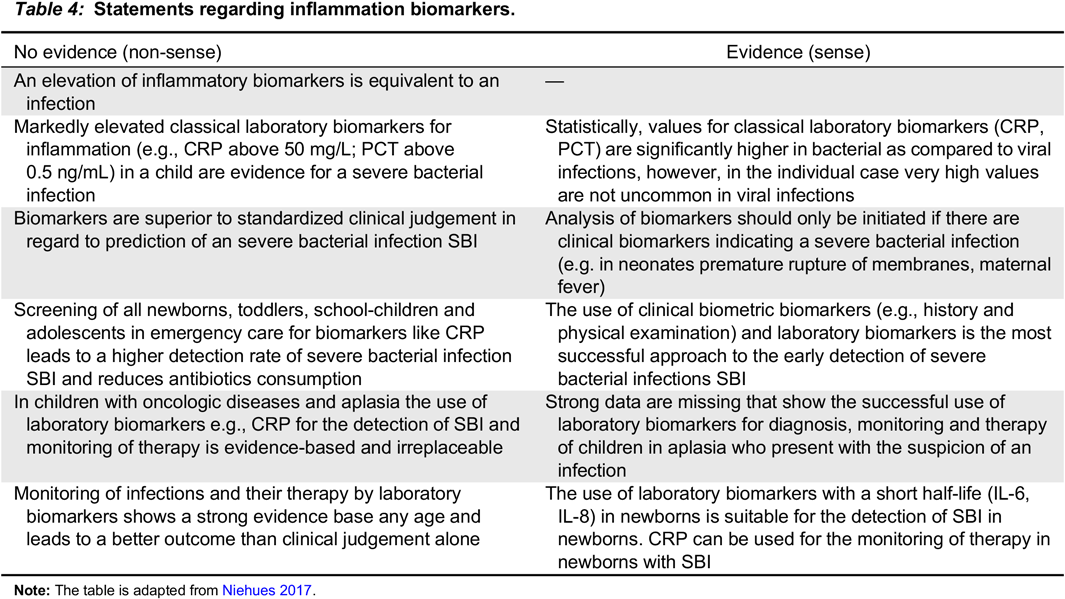
Note: The table is adapted from Niehues 2017.
List of abbreviations
- APP
- Acute-Phase-Protein
- APR
- Acute-Phase-Reaction
- ESR
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- CD
- Cluster of differentiation
- CRP
- C-reactive Protein
- CSF
- Cerebrospinal fluid
- CXCL8
- CXC-Motive-Chemokine Ligand 8 (Interleukin-8)
- D/PAMP
- Damage/pathogen-associated molecular pattern
- FcRγ
- Fc-Receptor-γ
- GBS
- Group-B-Streptococci
- G-CSF
- Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor
- GM-CSF
- Granulocyte-monocyte- colony stimulating factor
- IBI
- Invasive Bacterial Infection (Bacteremia, Sepsis, Meningitis)
- IFN
- Interferon
- IL
- Interleukin
- IP-10
- Interferon-gamma induced protein 10”
- LPS
- Lipopolysaccharide
- NPV
- Negative predictive value
- PC
- Phosphocholine
- pCAP
- Pediatric community-acquired pneumonia
- PCT
- Procalcitonin
- PPV
- Positive predictive value
- PRR
- Pattern recognition receptor
- RSV
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus
- SBI
- Severe bacterial infection (Sepsis, Meningitis, Appendicitis, Pneumonia, Osteomyelitis, Cellulitis, Bacterial Gastroenteritis, Complicated Urinary Tract Infection)
- TNF-α
- Tumor-Necrosis-Factor-α
- TRAIL
- Tumor necrosis factor apoptosis inducing ligand
- WBC
- White blood cells
Acknowledgements
REFERENCES
Information & Authors
Information
Published In

History
Copyright
Authors
Competing Interests
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Other Metrics
Citations
Cite As
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
There are no citations for this item
View Options
View options
Login options
Check if you access through your login credentials or your institution to get full access on this article.


