Introduction
Severe inflammatory colitis can also be associated with so-called monogenic disorders in humans and mice (
Kuhn et al. 1993;
Hugot et al. 2001;
Stoll et al. 2004;
Duerr et al. 2006;
Hampe et al. 2007;
Parkes et al. 2007;
Cho 2008;
Franke et al. 2008;
Kaser et al. 2008;
Moran et al. 2013). Loss of function mutations in
interleukin (IL) -2Rα (
Roifman 2000) and
FOXP3 (
Bennett et al. 2001) lead to uncontrolled inflammation such as severe enteritis, nephritis, endocrinopathy, or other autoimmune manifestations. A major underlying mechanism in these diseases is the paucity or dysfunction of T-regulatory cells (T-regs). T-regs suppress excess inflammatory responses after antigen-mediated activation of effector CD4+ T cells, including Th17 cells. In T-regs, activated STAT3 and FOXP3 co-operatively regulate a subset of genes that empower these cells with the ability to suppress Th17-cell-mediated inflammation (
Chaudhry et al. 2009). Critical for the induction of Th17 cell responses is the activation of STAT3 transcription factor downstream of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-21, and IL-23. Indeed, T-reg specific deletion of STAT3 results in a fatal Th17-cell-driven colitis in mice (
Chaudhry et al. 2011). Th17-cell-mediated inflammation is also controlled by IL-10. It has been demonstrated that the IL-10 receptor was required for T-reg mediated suppression of Th17-cell-driven colitis (
Huber et al. 2011). IL-10 is secreted by a variety of cell types, and it has been shown to limit the secretion of the pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) and IL-12.
Patients with exaggerated inflammation may benefit from hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). It was first demonstrated in IL-2Rα deficiency (
Roifman 2000) and thereafter in patients with mutations in
FOXP3. Recently, early experience with HSCT using modified conditioning in IL-10 pathway defects has been reported (
Kotlarz et al. 2012). However, the cohorts are very small, and long-term outcomes are yet to be established.
We report here our experience with full myeloablative conditioning followed by matched unrelated HSCT in a patient with IL-10R1 deficiency.
Methods
Data retrieval
The patient was treated primarily at the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Ontario. Consent was obtained from the patient and her parents for inclusion in the Canadian Centre for Primary Immunodeficiency (CCPID) Registry and tissue bank, which has been approved by the SickKids Research Ethics Board (protocol No. 1000005598). Data from medical records were compiled prospectively and retrospectively, and entered into the CCPID Registry.
Lymphocyte markers and T-cell proliferative responses
Blood mononuclear cells were obtained using Ficoll–Hypaque density gradient centrifugation and the surface phenotypes were determined using direct immunofluorescence with fluorescein isothiocyanate conjugated MoAbs anti-CD3, CD4, CD8, CD20, and CD56 (Coulter Instruments, Mississauga, Ontario). Analysis was performed on a Coulter EPICS V flow cytometer. Lymphocyte proliferation response to phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) was assessed by tritiated thymidine incorporation using the microtitre plate technique. All assays were performed in triplicate and compared with normal controls that were performed at the same time.
Analysis of T-cell receptor (TCR) repertoire
TCR Vβ families within CD4+ and CD8+ subpopulations were investigated using flow cytometry as previously described in
Roifman et al. (2006)Sequence analysis
The patient's genomic DNA was analyzed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification and direct sequencing of the IL-10R1 gene. PCR primers were designed to amplify a genomic DNA fragment between 30 and 60 bp upstream and downstream of each transcript exon of the IL-10R1 gene. The PCR conditioning consisted of 94 °C for 30 s, 55 °C for 30 s, and 68 °C for 2 min, for a total of 35 cycles using Elongase (Invitrogen).
PCR products were electrophoresed on 0.8% agarose gels. Each PCR fragment was then cut and purified using QIAquick Gel Extraction Kit (QIAGEN). For mutation detection, each purified PCR fragment was autosequenced with a DTCS Quick Kit using the same PCR primers (Beckman–Coulter CEQ8000).
Results
Case
The patient was born after a spontaneous vaginal delivery at 30 weeks gestation to nonconsanguineous parents of English descent. Family history was significant for thyroid disease in a maternal aunt and gestational diabetes in the mother. At the age of 3 weeks the patient was admitted to the hospital for periorbital cellulitis. It was noted she had a presumed candida infection of her skin on the back of her neck, both axillae, and groin areas with satellite lesions that responded to treatment with nystatin. At 4 weeks of age she suffered an exacerbation of cellulitis complicated by meningitis. She fully recovered after antibiotic therapy.
At 3 months of age she was readmitted for purulent left ear discharge. Cultures of the discharge grew
Staphylococcus aureus. At 4 months of age, she was admitted for extensive erythroderma that was most prominent on the head, neck, torso, and extremities (
Figure 1). Swabs of the skin lesion grew
Klebsiella pneumonia and
Enterococcus. It was noted she had enlarged lymph nodes in the axillae and groin. She responded partially to steroids in combination with topical antifungal treatment.
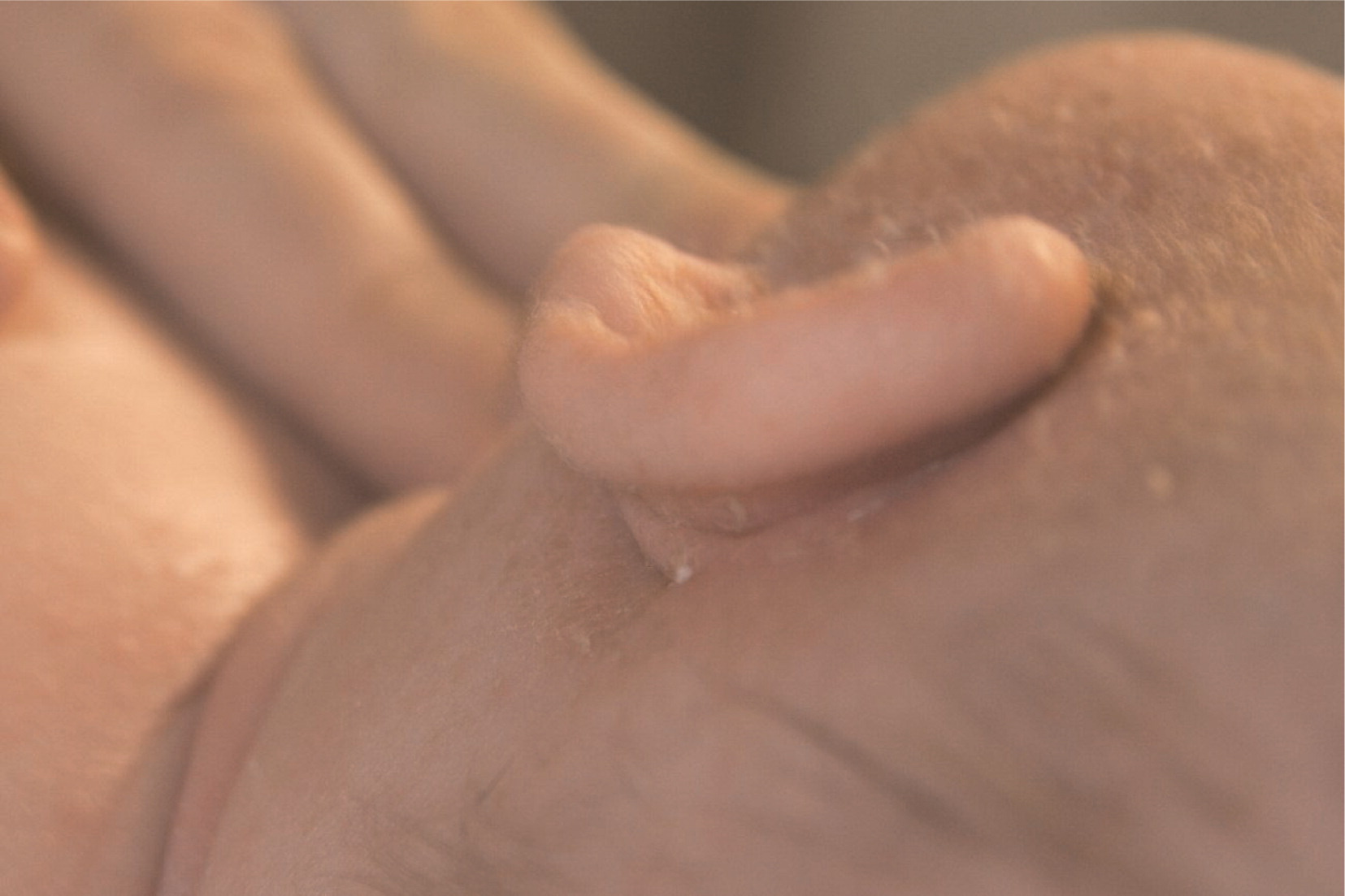
At 7 months of age she was admitted with a history of diarrhea and rectal bleeding that worsened over a period of 6 weeks. She was found to have perianal skin tags and fissures, leading to significant discomfort with stooling (
Figure 2). The diarrhea until this stage was intermittent.
From 8 to 12 months of age, she continued to have repeated episodes of fever and diarrhea that seemed to have responded initially to treatment with antibiotics. When symptoms became refractory to antibiotics she received sulfasalazine with apparent worsening of symptoms.
She was then placed on systemic steroids (1 mg·kg−1·day−1) with good response, but repeated attempts to wean her off steroids resulted in exacerbation of her symptoms.
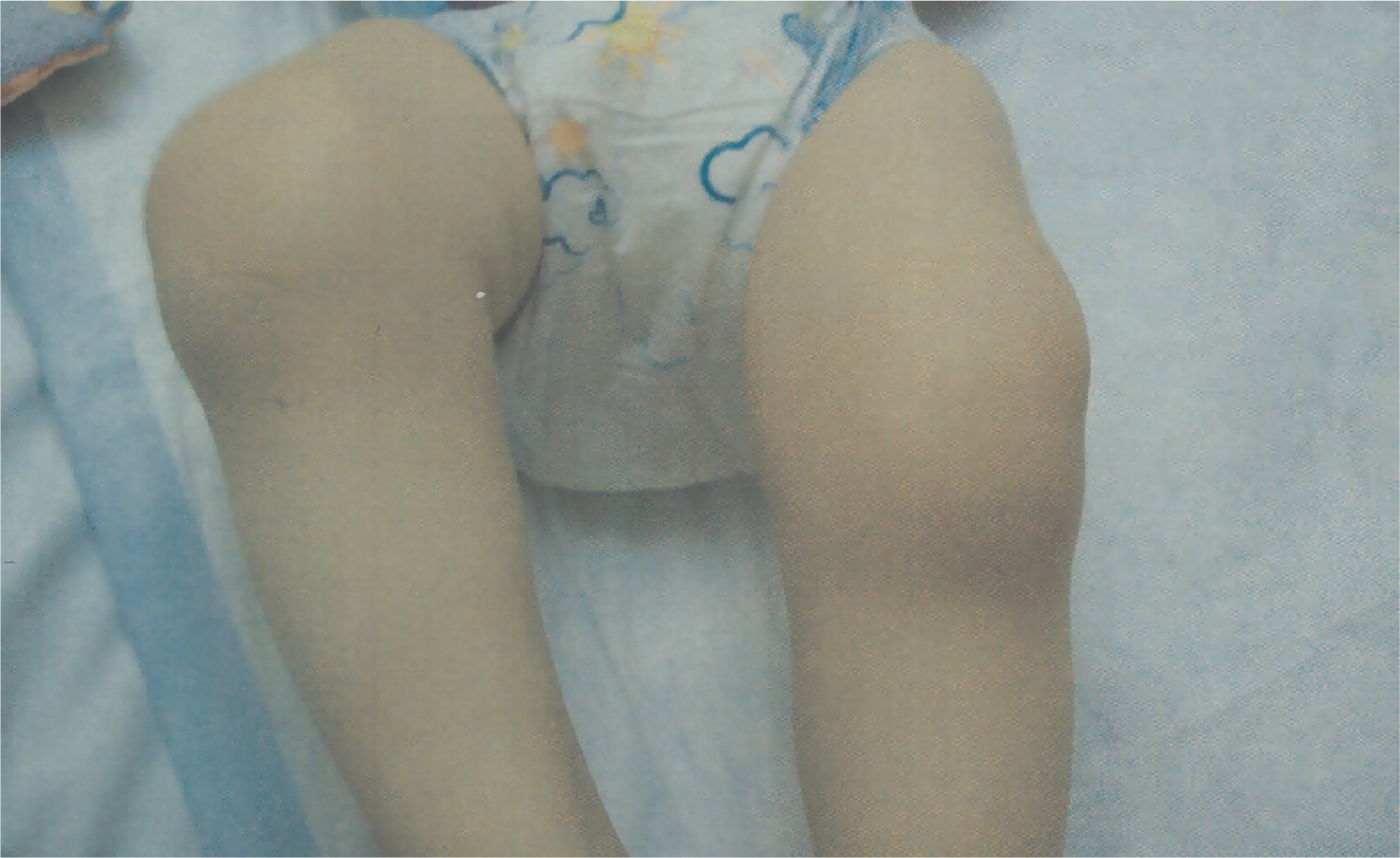
At 15 months of age she developed arthritis with significant effusions in her knees and involvement of her elbows (
Figure 3). Steroid joint injections controlled symptoms transiently and treatment with anakinra failed to control the arthritis.
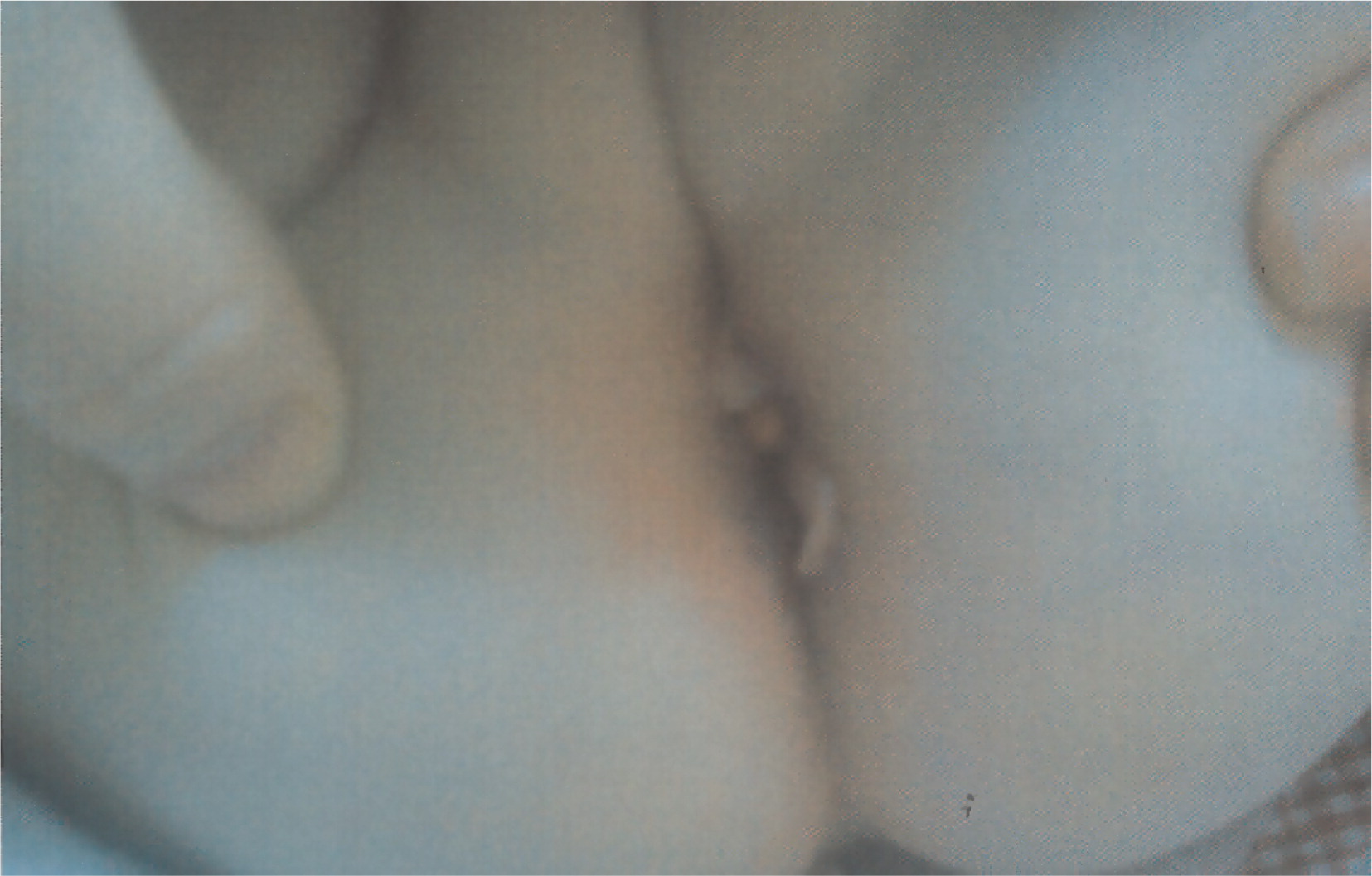
Over the ensuing 6 months she developed 4 perianal fistulae (
Figure 4). To allow for healing of the perianal area, a diverting ileostomy was performed. Unfortunately, in spite of this procedure, bloody diarrhea continued and the perianal area did not heal. Moreover, the surrounding area of the ileostomy became aggressively inflamed. Her deterioration and lack of adequate response to conservative treatment prompted consideration of HSCT.
Evaluation of immunity
The presentation with severe infections so early in life triggered a rigorous evaluation of the patient's immune system, with suspicion of a primary immunodeficiency. Her lymphocyte count was consistently high, ranging from 5 to 7 × 103 cells·µL−1. Numbers of CD4+ cells were consistently elevated between 4490 and 5106 cells·µL−1, with a relative paucity of CD8+ cells (7.5% of CD3+ cells). B-cell numbers were also elevated.
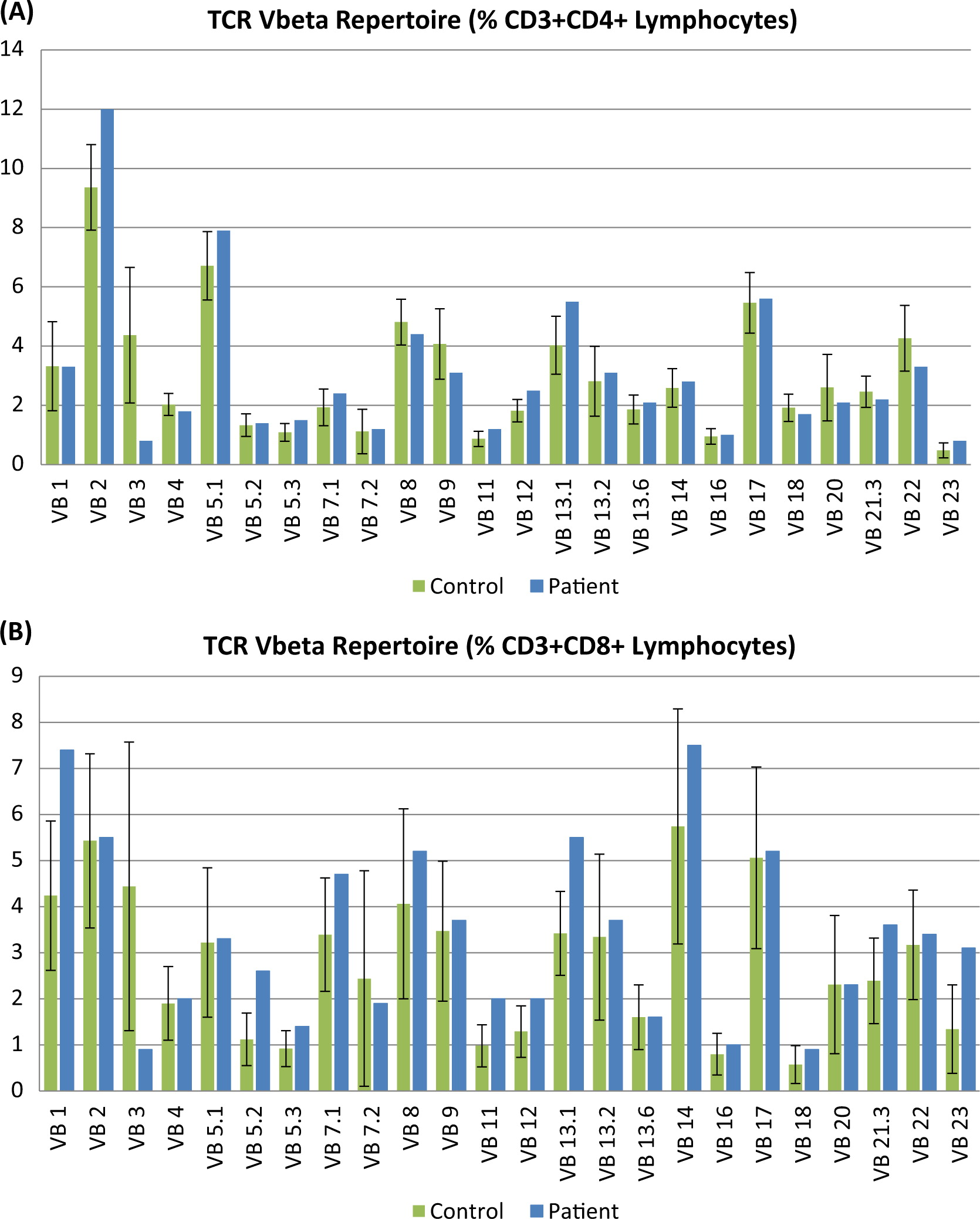
T-cell receptor excision circle levels were normal, suggesting adequate thymopoiesis. Evaluation of the TCR repertoire revealed clonal expansion of several Vβ families, reminiscent of autoimmune disorders (
Figure 5). Stimulation index of in-vitro responses to PHA were reduced compared with control samples, but this was mainly attributed to a high background, likely related to activated T cells.
Upon exposure to egg, the patient had an episode of cyanosis and breathing difficulties consistent with type 1 hypersensitivity reaction. A whole egg extract skin-prick test was strongly (+3) positive. ImmunoCAP–radioallergosorbent test (CAP–RAST) test to egg white and egg yolk were positive.
Accidental exposure to cow's milk triggered a severe episode of diarrhea and vomiting. Skin-prick testing performed at 13 months of age was strongly positive to fresh cow's milk (+4) and cow's milk extract (+3).
Genetic analysis
Sanger sequencing of
IL-10R1 revealed a homozygous mutation in intron 5 at the conserved GT splice donor site c.(688+2T > C) (
Figure 6). This mutation of the invariant dinucleotide GT at the 5′-splice donor site alters normal splicing and creates a cryptic splice site as previously described in
Moran et al. (2012).
The predicted aberrant protein contains only the extracellular domain of IL-10R1.
Description of colitis
Biopsies performed through colonoscopy at 8 months of age showed colonic mucosa that had mild architectural disarray of glands with focal branching but a well-preserved goblet cell population. The lamina propria showed a mild increase of mixed infiltration of inflammatory cells with focal aggregates of eosinophils. The surface epithelium showed mild exudates of neutrophils and fibrin, suggesting exudation into the lumen. There was no evidence of ulceration. The features suggested mild, acute nonspecific colitis.
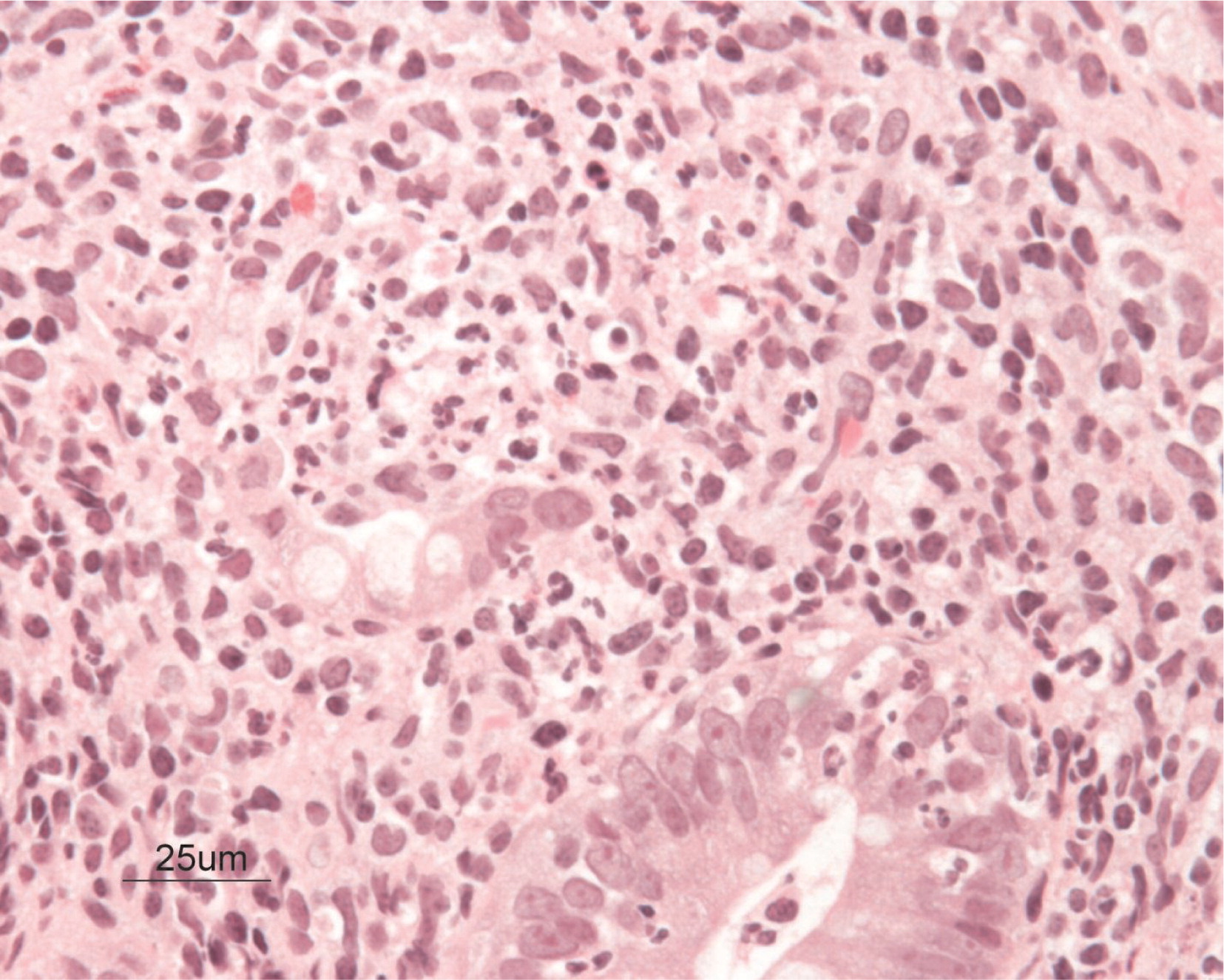
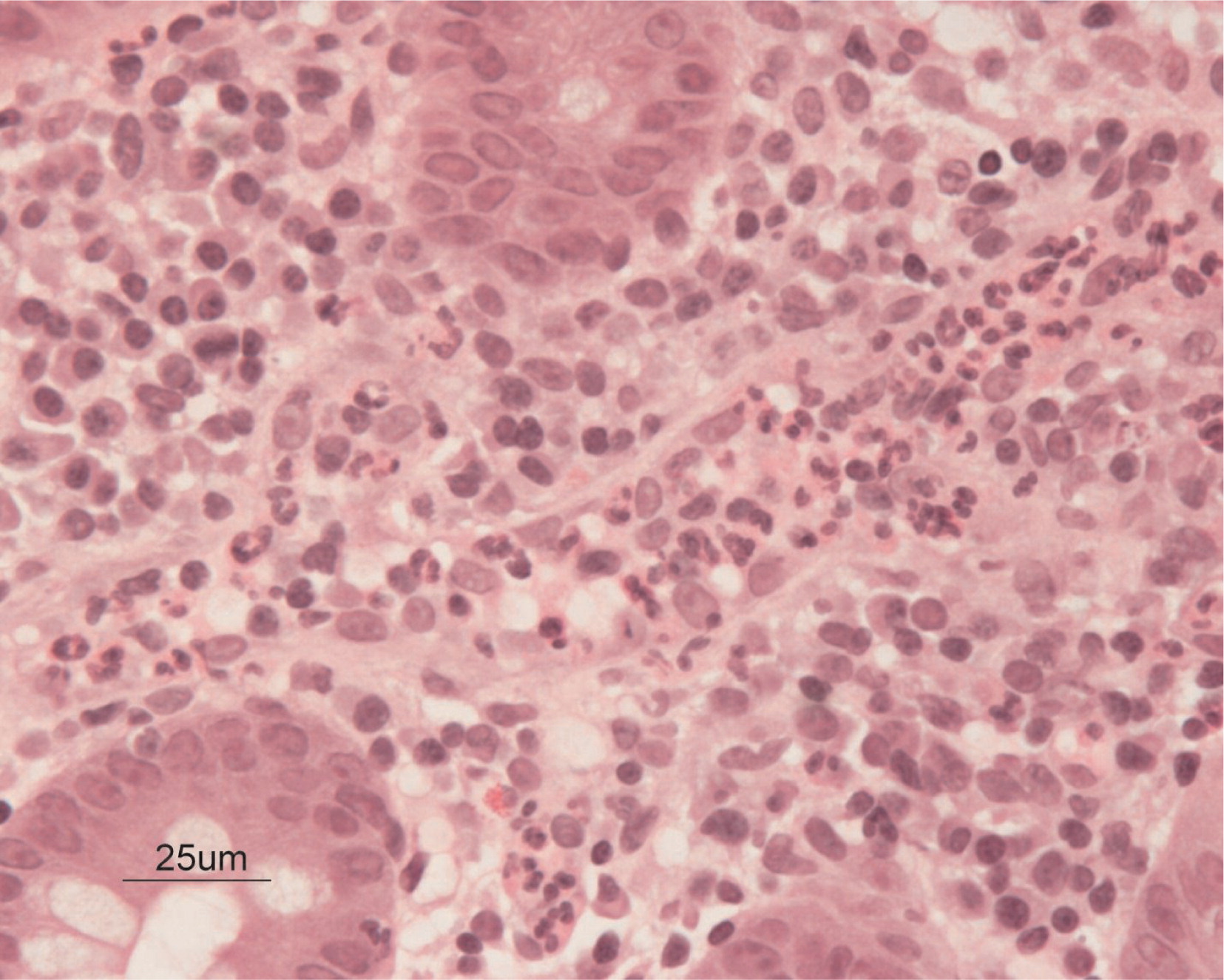
Biopsies obtained at 17 months of age showed that the glands throughout were generally elongated and showed reduction of goblet cell population. The most inflamed portion of the gut identified was in the cecum, where there were heavy aggregates of neutrophils in the lamina propria and crypt abscesses (
Figures 7 and
8). Focal and sporadic crypt abscesses were also noted in the descending and ascending colon, sigmoid, and rectum. There was continuous severe grade 3 colitis with multiple large serpiginous ulcers in the rectum and sigmoid colon.
Perianal examination revealed a long pedunculated skin tag and chronic fissures at multiple sites (
Figure 2).
Skin manifestations
A skin biopsy was performed in which the epidermis showed psoriasiform acanthosis, patchy parakeratosis associated with collection of neutrophils in the parakeratotic layer, and minimal exocytosis of lymphocytes and eosinophils. There were patchy foci of spongiosis associated with lymphocytes. An occasional necrotic keratinocyte was seen. The papillary dermis was edematous and had a mild-to-moderate perivascular and interstitial infiltrate of lymphocytes with fewer eosinophils and neutrophils. Special stains for bacterial and fungal organisms were negative. Immunohistochemical stains revealed loss of CD7 and paucity of CD8+ cells. The majority of the cells in the dermal infiltrate were positive for CD2, CD3, CD4, and CD5. Molecular immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor rearrangement studies revealed monoclonality in both cell types suggesting aberrant lymphocyte expansion or malignancy.
Hematopoeitic stem cell transplantation
With no human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-matched donor in the immediate family, we elected to use a 10/10 antigen matched unrelated donor (MUD). The patient received myeloablative conditioning with busulfan and cyclophosphomide as well as graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) prophylaxis with cyclosporine and prednisone. Engraftment was rapid, starting with neutrophils on day +9. Her last transfusion of red cells and platelets was on day +10 and day +16 post-transplantation, respectively.
The transplant course was uneventful with the exception of one major episode of gastrointestinal bleeding. Although GvHD was considered in the differential diagnosis, we elected not to add immunosuppressive agents and she subsequently recovered spontaneously. Abdominal pain, frequent stooling, and bloody diarrhea completely resolved within less than 1 month following transplantation. The perianal inflammation and fistulas also resolved. Doses of cyclosporine and steroids were gradually reduced and the severe cushingnoid features disappeared. At 5 months post-transplant her small bowel was surgically re-anastomosed and all incisions healed quickly.
Two years post-transplant, she maintained a robust engraftment with 100% donor cells in the circulation. Evaluation of the immune system revealed normal numbers of circulating CD3+ T cells as well as normal in-vitro responses to mitogens.
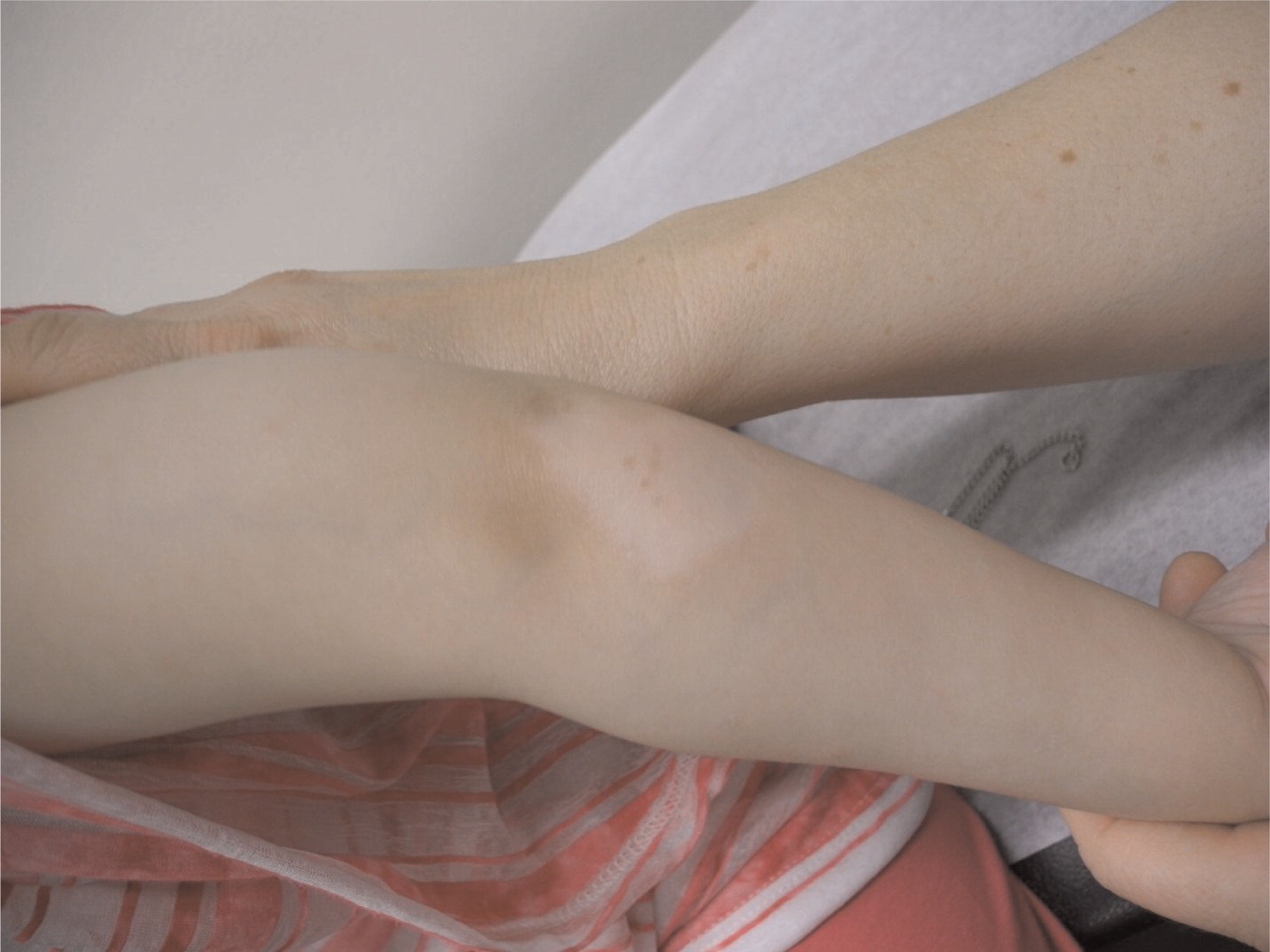
An attempt to discontinue steroid treatment resulted in a breakthrough of her joint inflammation. She complained again of morning stiffness, and on examination moderate effusions in the knees and wrists were noted. In addition, a large patch of skin hypopigmentation (vitiligo) was identified on her left elbow (
Figure 9).
Discussion
We reported here in detail the clinical course including HSCT of a patient with IL-10R1 deficiency. Because infantile colitis is frequently fatal in spite of medical treatments, attempts have been made to cure the condition with HSCT. Early studies in mice suggested that this might be a plausible approach (
Mottet et al. 2003). Indeed, 7 patients with IL-10R1 or IL-10R2 deficiency who received transplants from matched related or matched unrelated donors have been recently reported (
Kotlarz et al. 2012). Patients received nonmyeloablative conditioning and reported follow-up time is too short to draw any conclusions. However, 3 of 4 patients who received MUD had graft failure and needed a second infusion of stem cells. Nevertheless, improvement of gut symptoms appeared universal.
Because of the high frequency of acute GvHD in MUD transplants, we anticipated major complications in this patient, particularly because of the pre-existing severe enterocolitis. To ascertain sustained engraftment, our protocol included myeloablative conditioning with cyclophosphomide and busulfan. The combination of cyclosporine and prednisone was used for GvHD prophylaxis. Surprisingly, the post-transplantation course was uneventful with no GvHD. Severe colitis resolved completely within 4 weeks of transplantation. In contrast, weaning of steroids down to 10 mg every other day resulted, unexpectedly, in a breakthrough of symptoms such as morning stiffness and gradual increased swelling of knees and wrists. Intra-articular injections of steroids controlled symptoms transiently but the patient required systemic steroids to suppress joint inflammation.
It is not immediately clear why inflammation in the gut completely reversed after HSCT but arthritis did not. The resistance of arthritis to treatment with HSCT is intriguing. Based on the TH
1 T-cell abundance in the synovium, replenishing IL-10, which is a prototypic TH
2 cytokine, we would have predicted improvement of arthritis but this did not occur in our patient. This may suggest that this failure may not be related solely to availability of IL-10 in the joints as previously speculated in IL-10 treatment models for rheumatoid arthritis (
Smeets et al. 1999).
Moreover, in theory, all recipient T cells as well as macrophages should be substituted with donor cells after myeloablative conditioning followed by a HSCT. If this was achieved in our patient, as evidenced by the robust engraftment, then it would suggest that replacing T cells and macrophages may not be sufficient to arrest pre-existent inflammation in the joints. Although there is ample evidence for involvement of T cells in the process of the development of arthritis (
Stastny 1976;
Nepom et al. 1989;
Weyand et al. 1992), their role in propagation of the disease remains unclear. Indeed, one hypothesis for long standing disease that leads to a destructive phase is that this process may become independent of antigen stimulation and canonical immune responses (
Firestein and Zvaifler 1990). This process may be locally controlled by synoviocytes and osteoclasts, and it may be propagated by autocrine and paracrine systems involving IL-1, TNFα, GM-CSF, various chemokines, and other factors (
Firestein 2003). The fibroblast-like synoviocytes in the intimal lining produce factors that can maintain inflammation by activating cells in their environment. Neighbouring cells are induced to express and secret other cytokines, metalloproteinases, prostaglandins, and nitric oxide contributing to the process (
Firestein and Zvaifler 1990;
Firestein 2003).
An alternative possibility is that recipient local intra-articular macrophages that play a major role in inflammation may have survived the myeloablative conditioning. More speculative is the remote event that donor cells contained genetic aberrations known to render individuals more susceptible to arthritis.
Regardless of the reason, it is important to educate physicians as well as patients about the possibility of a failure to reverse some autoimmune manifestations in these disorders.
In summary we demonstrated here that: (i) HSCT with a MUD can be safely and successfully used to replace the immune system in IL10R1 deficiency, (ii) the potentially fatal colitis resolved completely within weeks of transplantation, (iii) myeloablative conditioning enabled a robust engraftment and immune reconstitution without toxicity, and (iv) pre-existing arthritis was not reversed.