Chronic granulomatous disease 2018: advances in pathophysiology and clinical management
Abstract
Introduction to chronic granulomatous disease (CGD)
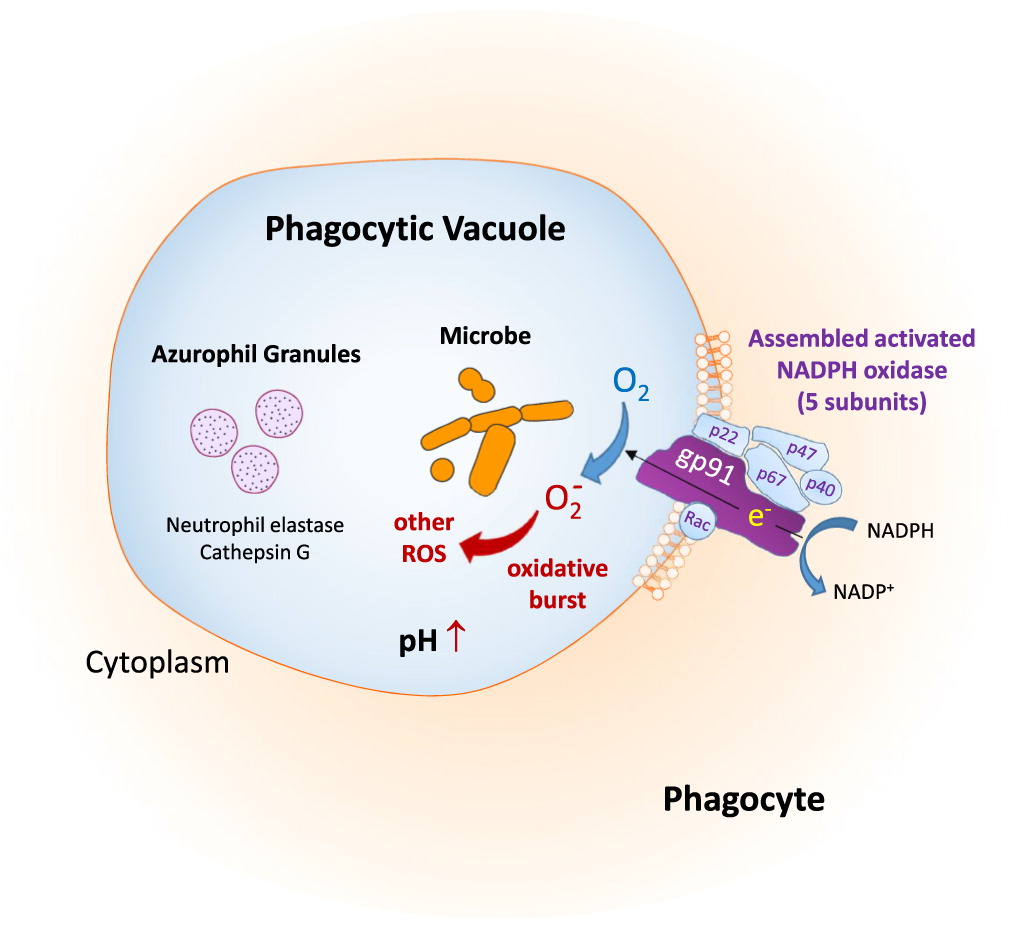
Etiology and pathophysioloy of the disease
Genetic defects
Impaired microbial killing

Excessive inflammation
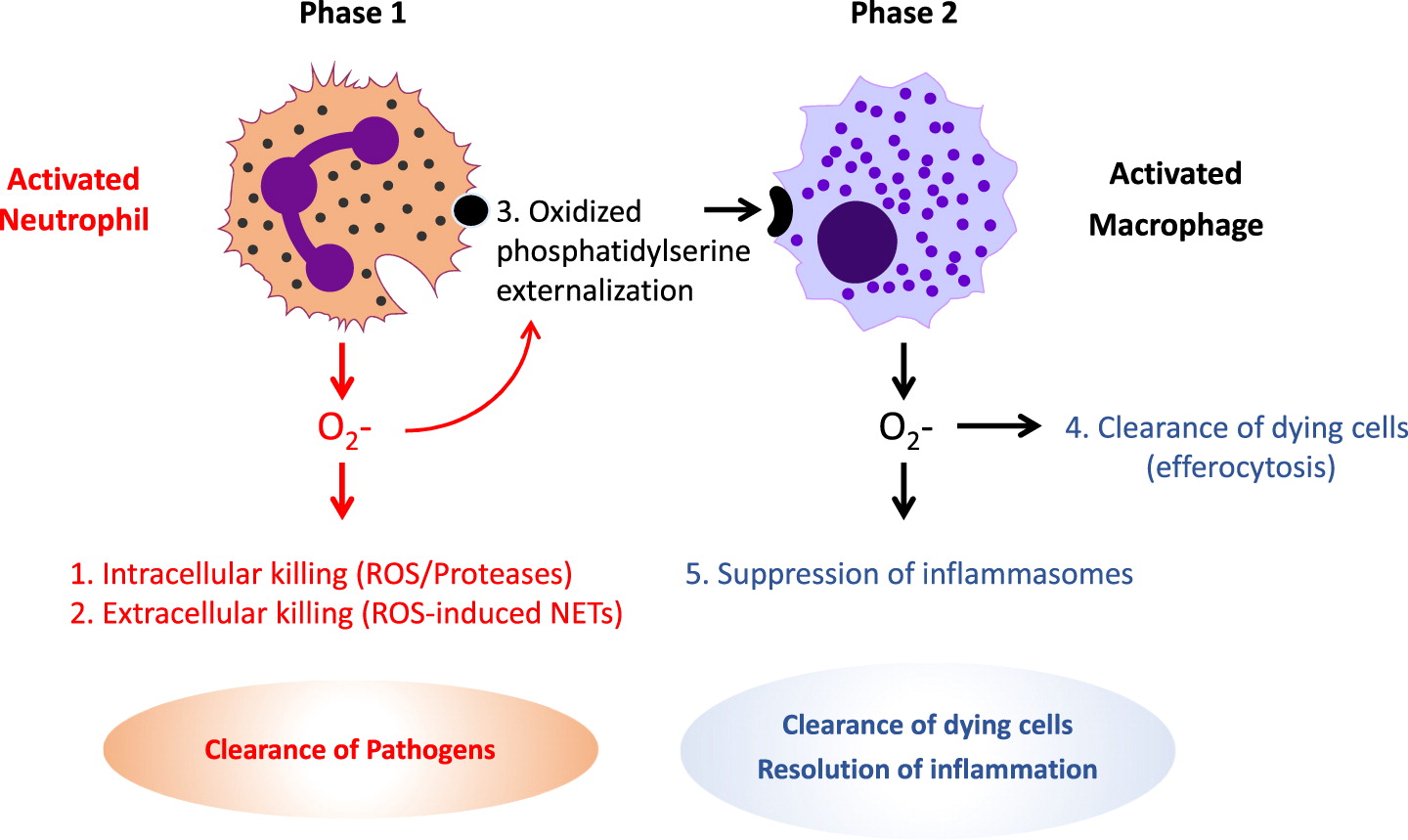
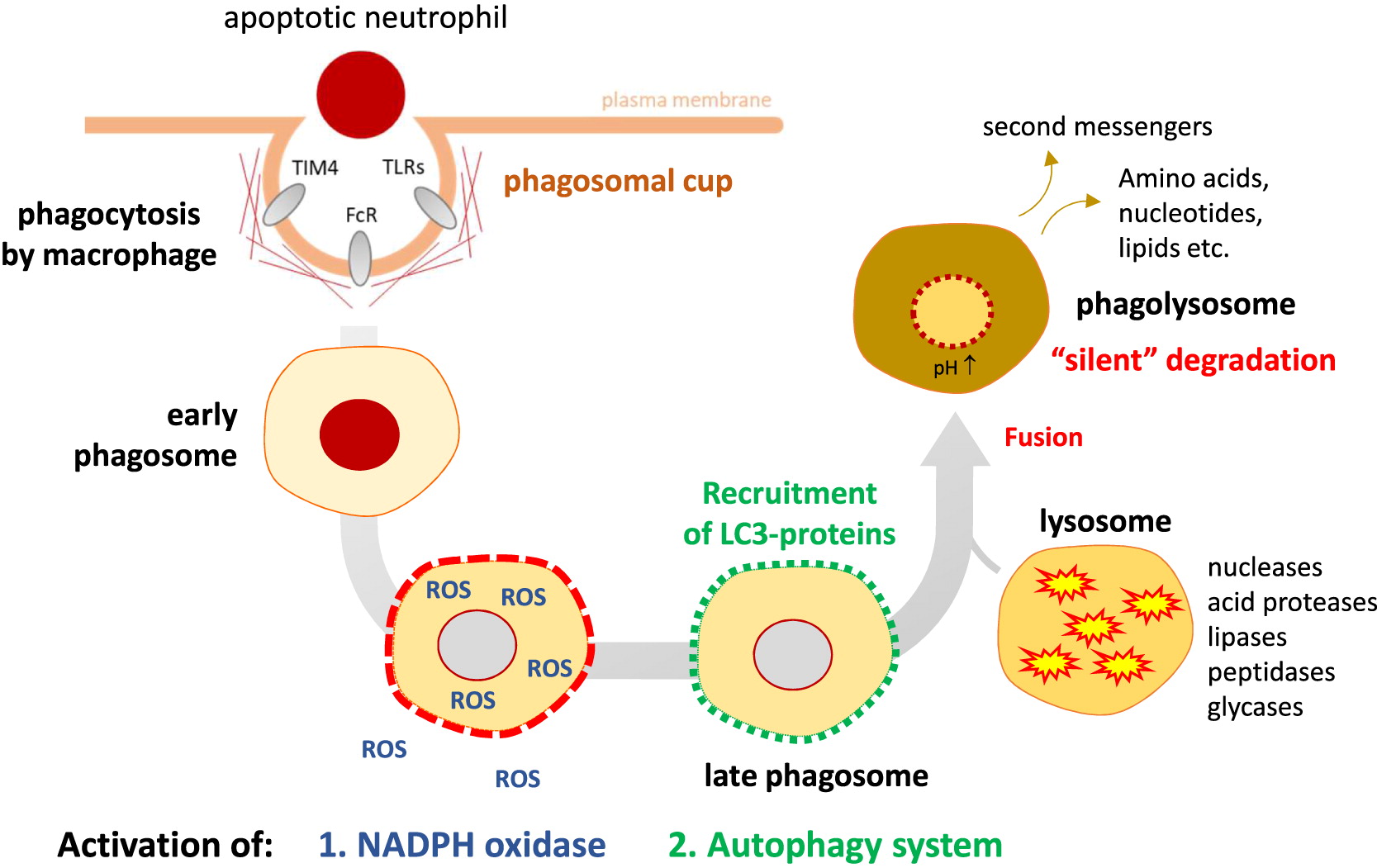
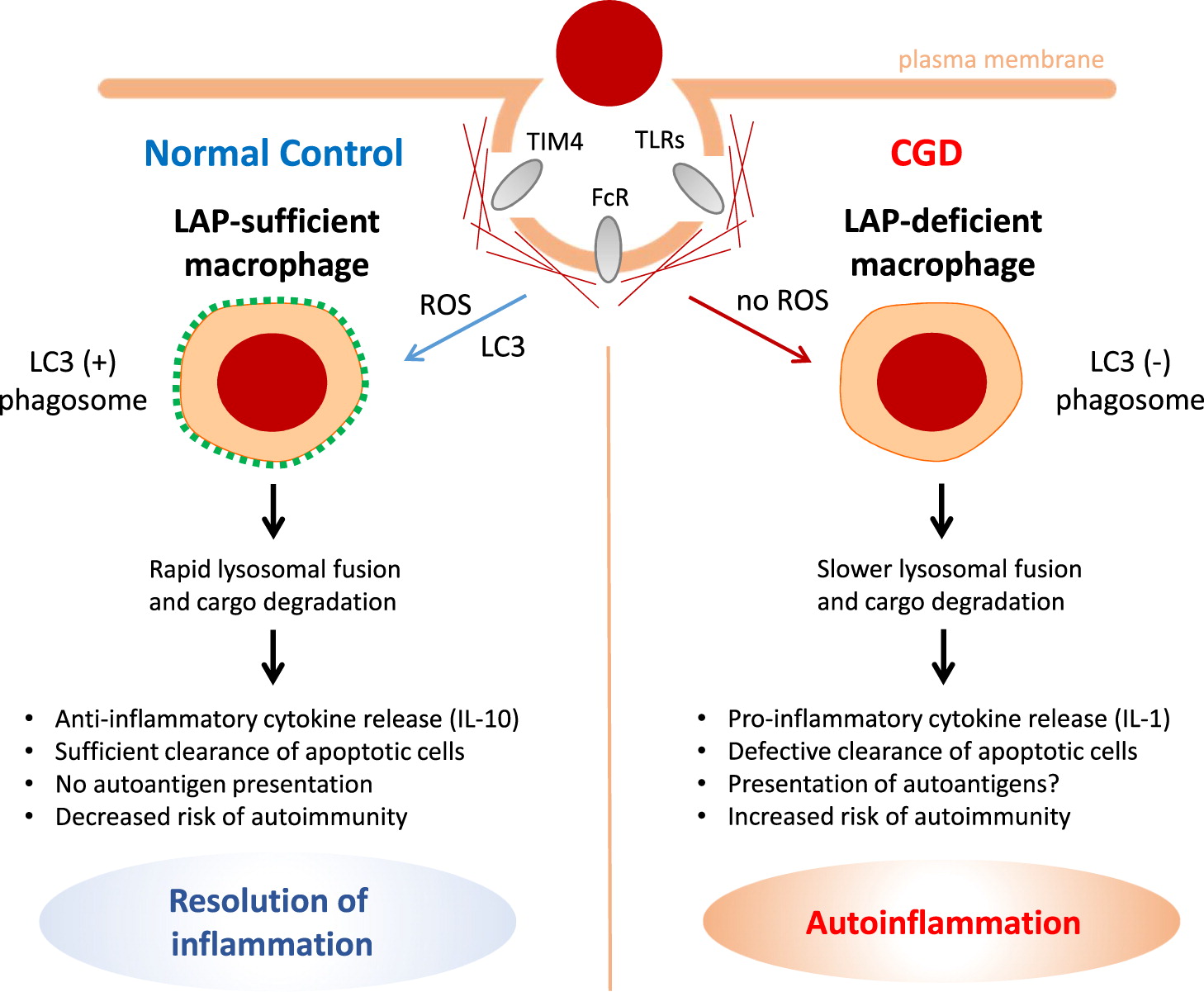
Clinical manifestations of CGD
Bacterial and fungal infections
Inflammatory manifestations
Clinical presentation in adults
Clinical presentation in carriers of X-linked CGD
Conventional treatment of CGD
General health care
Antimicrobial prophylaxis
Treatment of serious infections
Treatment of inflammatory complications
Curative treatments
Allogeneic HSCT
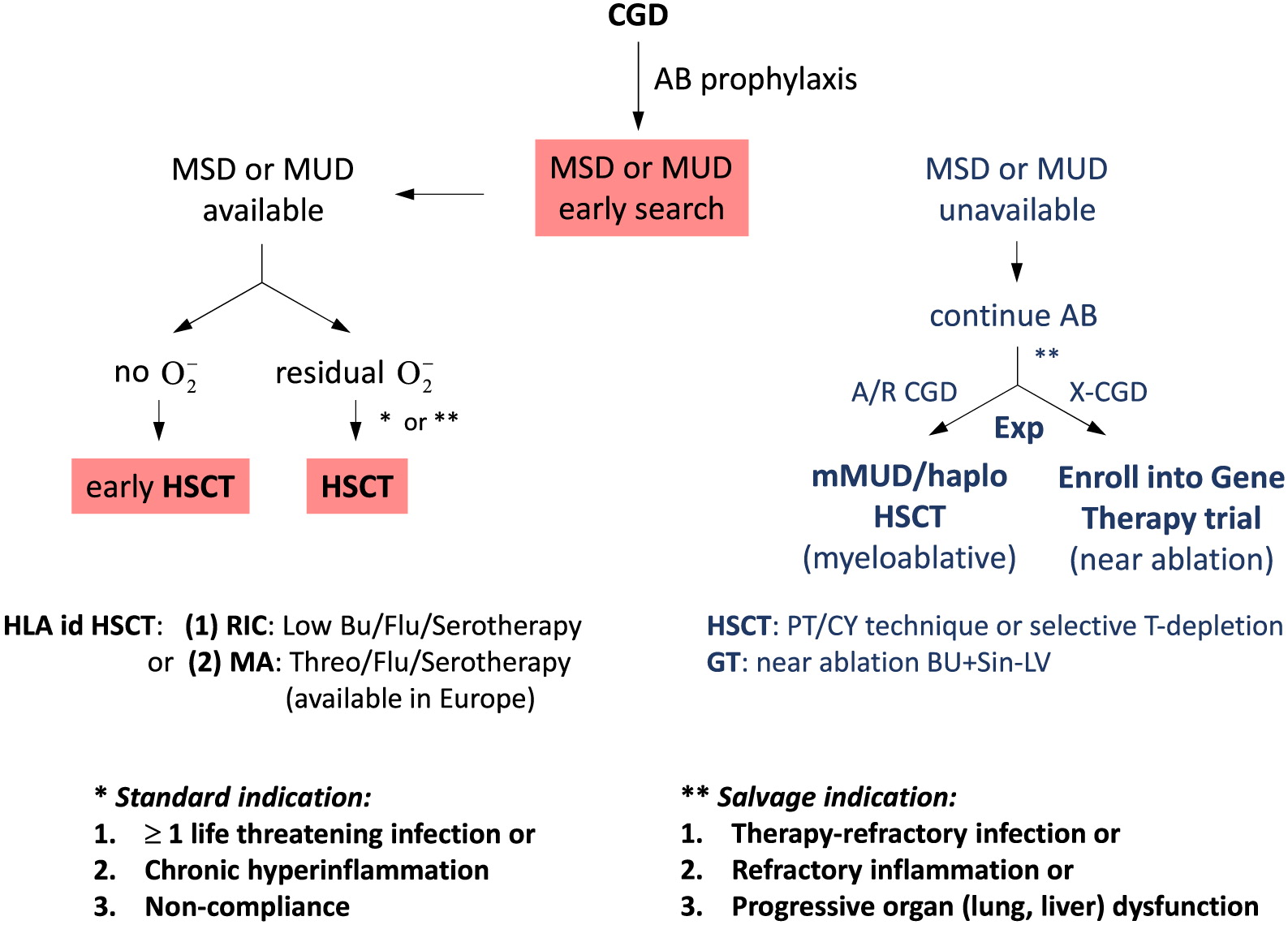
Therapies under investigation
HLA-haploidentical HSCT
Stem cell gene therapy
Abbreviations
- AR
- autosomal recessive
- CGD
- chronic granulomatous disease
- GT
- gene therapy
- GvHD
- Graft-versus-host disease
- HSCT
- hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- IFNγ
- interferon gamma
- IL-1β
- interleukin 1 beta
- MA
- myeloablation
- NET
- neutrophil extracellular trap
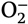
- superoxide anion
- oxPS
- oxidized phosphatidylserine
- PHOX
- phagocyte NADPH oxidase
- PIO
- pioglitazone
- PT/CY
- post-transplant cyclophosphamide
- RIC
- reduced intensity conditioning
- ROS
- reactive oxygen species
- TDM
- targeted drug monitoring
- TMP-SMX
- trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
- TNFα
- tumor necrosis factor alpha
- XR
- X-linked recessive
Acknowledgements
REFERENCES
Information & Authors
Information
Published In

History
Copyright
Authors
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Other Metrics
Citations
Cite As
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
There are no citations for this item
View Options
View options
Login options
Check if you access through your login credentials or your institution to get full access on this article.


