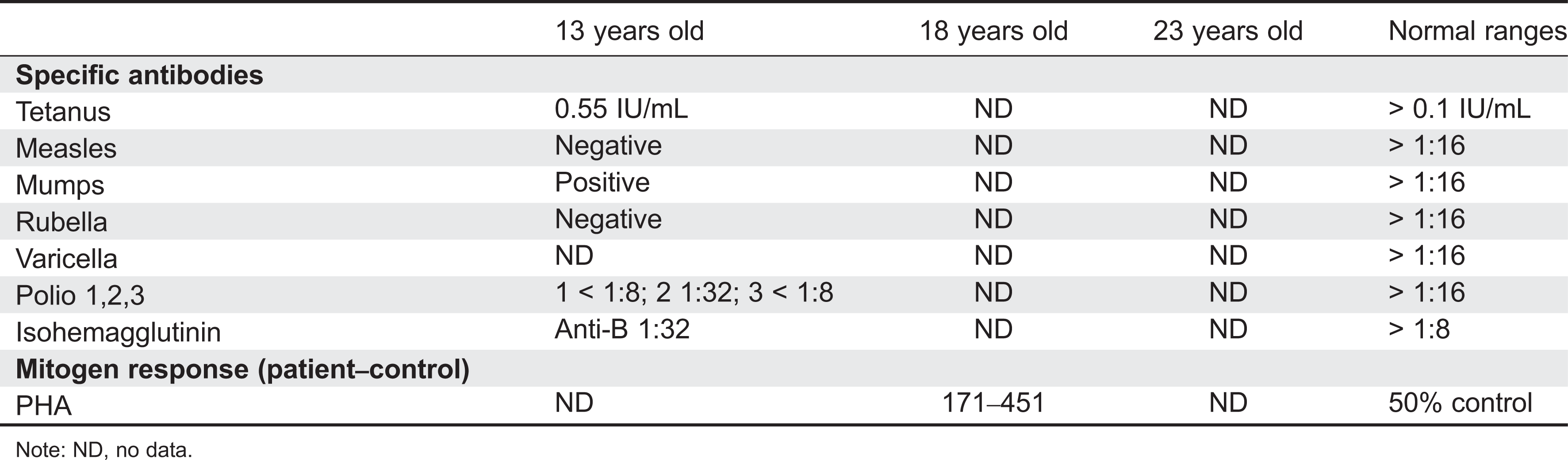Introduction
Hyper IgE syndrome (HIES) is classified as a well-defined syndrome with associated primary immunodeficiency (
Al-Herz et al. 2011). HIES can be sporadic or familial, with both autosomal dominant and recessive cases described. The autosomal dominant form of HIES is most commonly caused by a mutation in signal transduction and activators of transcription 3 (
STAT3) (
Holland et al. 2007;
Minegishi et al. 2007), whereas the less common autosomal recessive forms are linked to mutations in dedicator of cytokinesis 8 (
DOCK8) (
Engelhardt et al. 2009;
Zhang et al. 2009) and tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) (
Minegishi et al. 2006).
The human
DOCK8 gene consists of 46–48 exons located on chromosome 9 (
Su 2010) and is a member of the DOCK180 superfamily of guanine nucleotide exchange factors, which interacts with Rho GTPase (
Ruusala and Aspenstrom 2004). The exact function of
DOCK8 is unknown, but research supports its involvement in regulating cytoskeletal rearrangements that are essential for cellular structure, migration, and adhesion (
Meller et al. 2005). Defects in
DOCK8 have been shown to affect the immune system in numerous ways leading to a combined immunodeficiency.
DOCK8 is involved in T-cell survival and the maintenance of CD8 T-cell memory (
Lambe et al. 2011). Impaired T-cell activation (
Zhang et al. 2009) and reduced numbers of T-cell excision circles (TRECS) suggest impaired thymopoiesis with possible restricted diversity of T-cell repertoire in the periphery (
Dasouki et al. 2011). Furthermore, patients also have defective Th17 differentiation and long-term persistence (
Al Khatib et al. 2009). Murine studies have shown that
DOCK8 mutant B cells were unable to form marginal zone B cells or persist in germinal centers leading to impairment in affinity maturation of T-cell dependent antibody responses (
Randall et al. 2009). It has also been described that Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) responses were considerably lower in
DOCK8-deficient B cells and that
DOCK8 functions as an adaptor in the TLR9–MyD88 signaling pathway in B cells (
Jabara et al. 2012). Recently,
DOCK8 deficiency has been shown to be associated with an increased production of autoantibodies, defective B cell tolerance, and quantitative and qualitative deficiencies in regulatory T cells (
Janssen et al. 2014a). Lastly, the development and survival of mature natural killer T cells are impaired in
DOCK8-deficient mice (
Crawford et al. 2013).
HIES secondary to
DOCK8 mutation has a more severe phenotype compared with the
STAT3 mutations. Patients with
DOCK8 mutations commonly present with significant viral cutaneous infections, sinopulmonary infections, and allergic diseases such as asthma, environmental allergies, and food allergies (
Zhang et al. 2009;
Alsum et al. 2013). This patient population lacks the extra immune abnormalities observed in
STAT3 mutations, such as musculoskeletal and dental abnormalities and the characteristic coarse facial appearance. Early diagnosis of
DOCK8 mutation patients is critical, as hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is offered to selected patients as a curative therapy.
Results
A 13-year-old male patient from a nonconsanguineous Caucasian family was initially referred for intermittent diarrhea, recurrent molluscum contagiosum, skin abscesses, eczematous skin lesions, and lymphopenia. At 9 years of age, this patient developed diarrhea occurring every 3–4 months, lasting for 1 week, with as many as 10 episodes per day. The diarrhea episodes were associated with severe abdominal cramping and mucus with absence of blood in stools or associated fever. Infectious history was significant for severe molluscum contagiosum to the trunk and extremities beginning at childhood. Additional viral infections included extensive herpes simplex virus infection limited to the skin at 23 years of age. A history of bacterial infections was significant for 2 skin abscesses located on the left arm managed with incision and drainage at 13 years of age, and acute otitis media managed with oral antibiotics at 15 years of age. In addition to cutaneous infections, he had widespread nummular eczematous lesions over his extremities, trunk, and scalp beginning at 7 years of age. These lesions were initially diagnosed as psoriasis and managed with topical corticosteroids with minimal benefit. He had abnormal fingernails described as pitted and hypertrophied with associated peeling and crusting around the nailbed. Additional significant findings included intermittent oral ulcers and left-sided Bell's palsy. There was no history of allergic diseases.
Family history included a healthy nonconsanguineous mother and father, both from the Netherlands. He has an older sister who is healthy. The paternal grandmother had extensive atopic dermatitis. On the maternal side there was a female first cousin with vitilago and another first female cousin with leukemia diagnosed at 12 years of age.
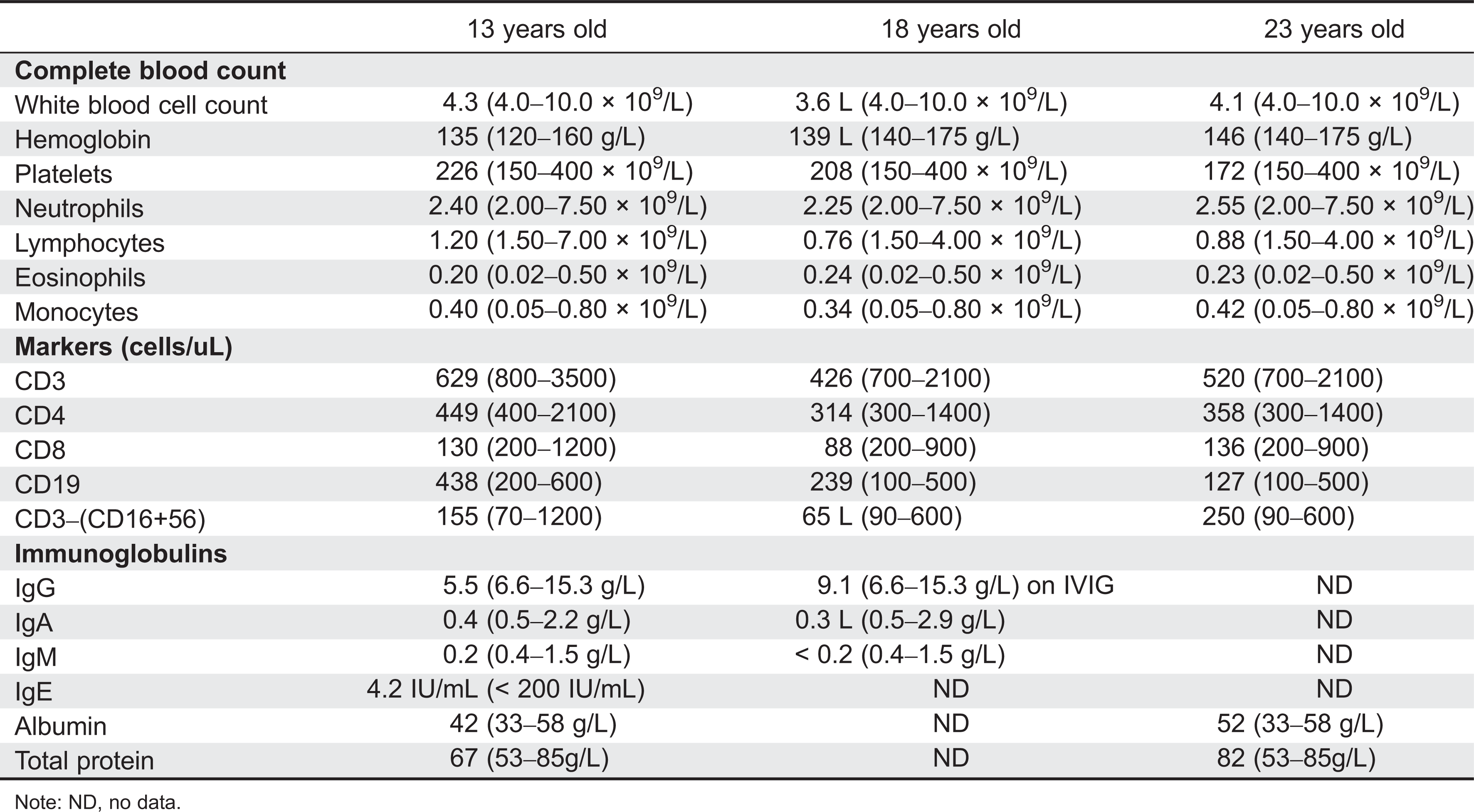
Initial immune investigations were completed at 13 years of age (
Tables 1 and
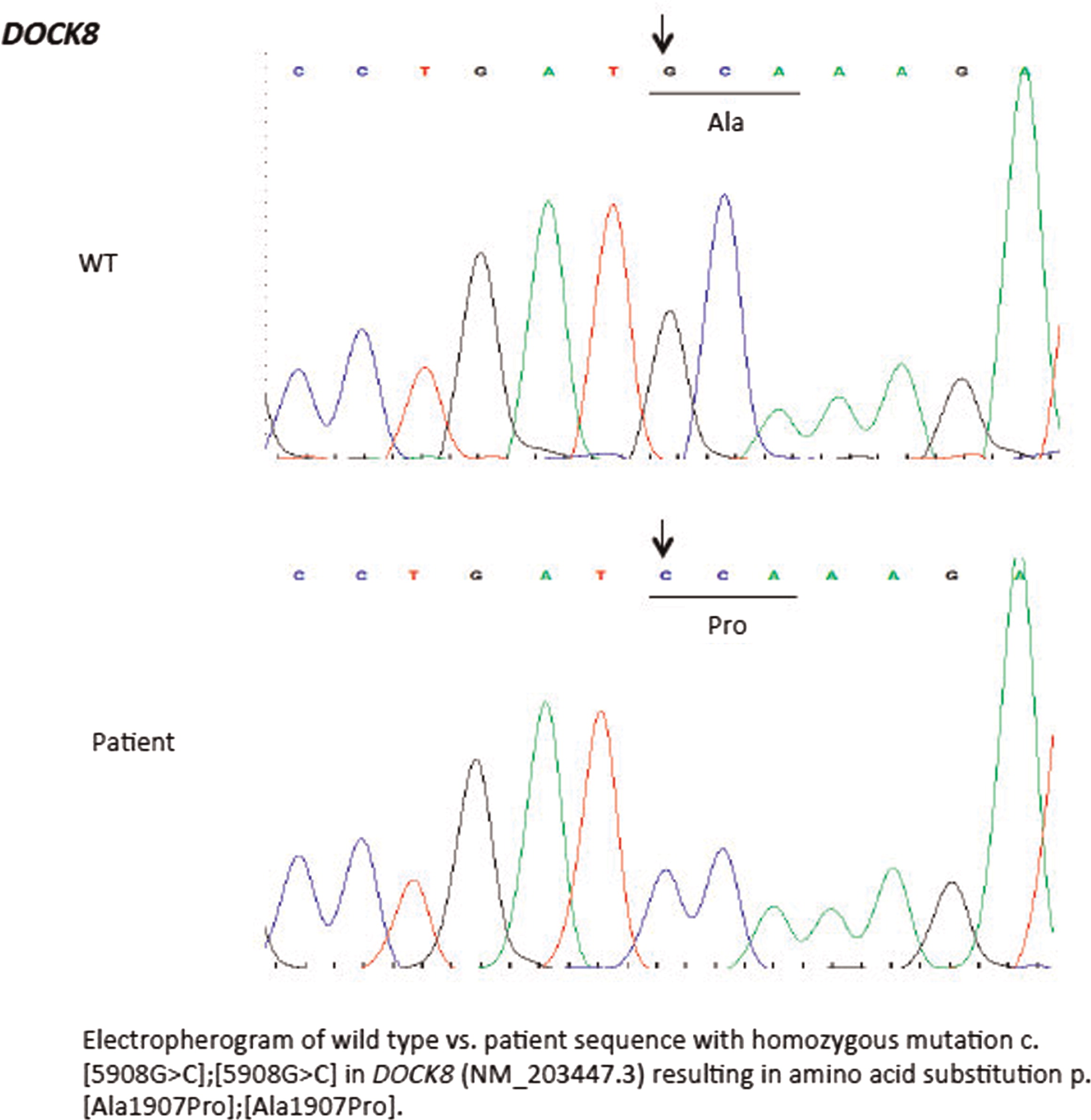
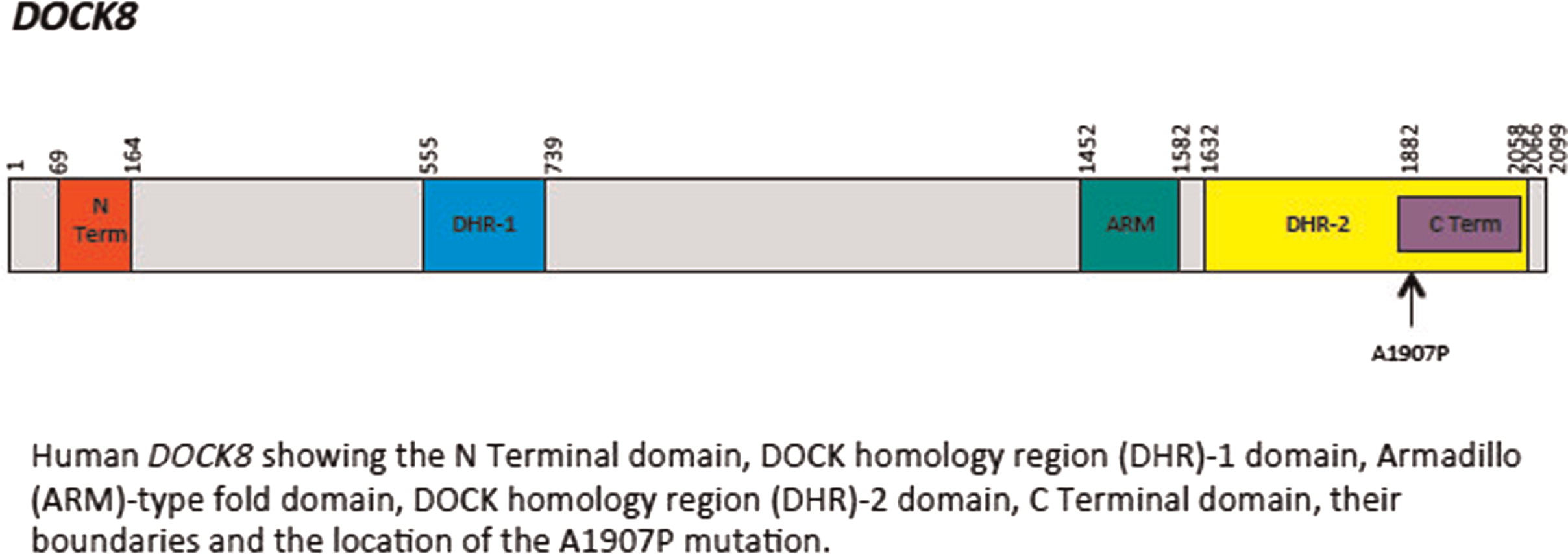
2). There was evidence of poor specific antibody response to tetanus (pre-vaccine titer 0.55 IU/mL, post-vaccine titer 0.85 IU/mL) and pneumococcus (post-vaccine titer 31.2 mg/L). Based on the poor specific antibody response, monthly intravenous immunoglobulin was started at 14 years of age. Genetics confirmed novel
DOCK8 mutation exon 45 aa1970, c.5908 G > C change alanine to proline homozygous change A1970 to P1970 (
Figures 1 and
2).
Discussion
The characteristic infectious and noninfectious features of
DOCK8 mutation associated HIES are described in our patient with a novel mutation. As demonstrated in our patient,
DOCK8 mutations lead to a number of cutaneous findings such as viral cutaneous infections secondary to molluscum contagiosum, herpes simplex virus (HSV), varicella-zoster virus, and human papillomavirus plus recurrent
Staphylococcus aureus skin infections (
Zhang et al. 2009). These infections can result in eczema herpeticum, chronic ulcerating orolabial or angogenital HSV infections, or HSV keratitis. The susceptibility to viral cutaneous infections is likely secondary to multiple factors including impaired CD8 T-cell memory response and reduced production of interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor α by CD8+ T cells in
DOCK8-deficient patients (
Zhang et al. 2009;
Chu et al. 2012). In addition,
DOCK8 may play a role in leukocyte migration to infected skin, and the breakdown of the epidermal barrier from dermatitis can predispose patients to viral infections (
Zhang et al. 2010;
Chu et al. 2012). Mucocutaneous candidiasis is less common in
DOCK8 patients compared with those with
STAT3 mutations (
Chu et al. 2012).
Similar to
STAT3 mutations,
DOCK8 deficiency can be difficult to differentiate from severe atopic dermatitis and other dermatitis, especially with higher rates of other allergic diseases such as food allergy also occurring with
DOCK8 mutations. A recent study concluded that CD3 and CD4 T-cell lymphopenia with decreased naïve CD8 T cells and decreased memory B cells is strongly suggestive of
DOCK8 deficiency rather than severe atopic dermatitis (
Janssen et al. 2014b).
Sinopulmonary infections such as recurrent otitis media, sinusitis, and pneumonias are frequently observed and can be associated with complications such as bronchiectasis (
Zhang et al. 2009;
Alsum et al. 2013). Our patient had a past history of acute otitis media. Various pathogens have been associated with pneumonia including
Streptococcus pneumonia, Haemophilus influenza, adenovirus, and respiratory syncytial virus as well as eosinophilic lung disease (
Zhang et al. 2009;
Tsuge et al. 2014). Recurrent sinopulmonary infections experienced in our patient and others with
DOCK8 mutation are consistent with the humoral immune abnormalities identified. Opportunistic infections including
Pnemocystis jiroveci and vaccine strain varicella-zoster virus induced central nervous system vasculopathy can occur, although they are less frequent (
Zhang et al. 2009;
Sabry et al. 2014). Diarrhea, which has been described in other patients with
DOCK8 (
Dinwiddie et al. 2013), was a significant complaint for our patient. Diarrhea can be secondary to infections such as salmonella, giardiasis, and norovirus (
Sanal et al. 2012). Other gastrointestinal involvement includes cryptosporidium-associated liver disease (
Al-Herz et al. 2012;
Shah et al. 2014). Additional features described in
DOCK8 patients include neurologic complications such as vasculitis, aneurysms, and central nervous system lymphoma, sclerosing cholangitis, and granulomatous soft tissue lesions (
Engelhardt et al. 2009;
Al-Herz et al. 2012;
Sanal et al. 2012).
Unlike patients with
STAT3 mutations, many patients with
DOCK8 mutations also have significant allergic diseases such as food allergy causing anaphylaxis, environmental allergies, and asthma (
Zhang et al. 2009). Eosinophilic esophagitis has also been reported (
Zhang et al. 2009). Increased rates of allergic diseases are likely secondary to increased Th2 CD4 T cells (
Lambe et al. 2011). Patients are often found to have high serum IgE and eosinophilia as the result. Although a common finding, our patient did not show any signs of allergic diseases.
Similar to many other primary immunodeficiencies,
DOCK8 is associated with higher rates of autoimmunity and malignancy. In patients with long-standing cutaneous viral infections, vulvar, facial, and anal squamous cell carcinomas can occur (
Zhang et al. 2009). Lymphoid malignancies such as Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) negative diffuse B-cell lymphoma, EBV-positive Burkitt lymphoma, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma are also noted (
Zhang et al. 2009). It has been suggested that impaired CD8 T cells in
DOCK8 deficiency may lead to impaired tumor surveillance resulting in an increased susceptibility to malignancies (
Zhang et al. 2009). Specific autoimmune conditions reported include autoimmune hemolytic anemia, colitis, vasculitis, uveitis, and systemic lupus erythematous (
Al-Herz et al. 2012;
Alsum et al. 2013;
Jouhadi et al. 2014). It is possible that the oral ulcers and Bell's palsy experienced by our patient was an autoimmune manifestation.
Common laboratory findings include lymphopenia, eosinophilia, elevated IgE and low IgM, decreased T- and B-cell numbers, variable impaired responses to mitogen stimulation, and poor antibody response. Our patient had lymphopenia affecting mostly CD8 T cells and low immunoglobulin levels. He also had evidence of poor function low mitogen stimulation response and poor specific antibody production. He did not have eosinophilia or elevated IgE.
There is growing consensus that HSCT should be offered to patients before significant infections with associated complications and development of malignancy occur (
Bittner et al. 2010;
Barlogis et al. 2011;
Gatz et al. 2011;
McDonald et al. 2012;
Metin et al. 2012). Patients with impaired antibody production may benefit from immunoglobulin replacement to reduce the frequency of sinopulmonary infections. Management of cutaneous manifestations in this patient population is difficult. Medications used to improve dermatitis such as topical corticosteroids can make cutaneous viral infections worse (
Chu et al. 2012). Systemic antiviral medications are used for cutaneous viral infections although resistance has occurred, whereas topical treatments are generally not effective given the extent of the disease (
Chu et al. 2012). Interferon alpha has been used with variable success for cutaneous viral infections and tumorous herpes simplex blepharoconjunctivitis (
Keles et al. 2014;
Papan et al. 2014). Bleach baths and topical antibacterial medications are helpful to control
Staphylococcal aureus colonization. All patients require sun protection given the predisposition for skin malignancy and careful monitoring for the development of malignancy.
Overall, DOCK8 deficiency is a rare combined primary immunodeficiency characterized by recalcitrant cutaneous viral infections, recurrent sinopulmonary infections, allergic diseases, autoimmunity and malignancy with associated eosinophilia, elevated IgE, and poor number and functioning of both T and B cells. Patients with these features should be investigated for possible DOCK8 mutations. Our data presented expands the spectrum of DOCK8 mutations.